In silico prediction and experimental evaluation of potential siRNAs against SARS-CoV-2 inhibition in Vero E6 cells
- PMID: 35493709
- PMCID: PMC9040457
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.102049
In silico prediction and experimental evaluation of potential siRNAs against SARS-CoV-2 inhibition in Vero E6 cells
Abstract
Objective: The acute cases of pneumonia (COVID-19) were first reported from China in December 2019, and the pathogen was identified as SARS-CoV-2. Currently, many vaccines have been developed against this virus by using multiple genes, applying different platforms, and used for the vaccinations of the human population. Spike protein genes play an important role in host cell attachment and viral entry and have been extensively used for the development of vaccine and antiviral therapeutics. Short interfering RNA is also known as silencing RNA and contribute a significant role to regulate the expression of a specific gene. By using this technology, virus inhibition has been demonstrated against many viral diseases.
Methods: In this work, we have reported the Insilico prediction, designing, and experimental validation of siRNAs antiviral potency against SARS-CoV-2-S-RBD. The siDirect 2.0 was selected for siRNAs prediction, and secondary structure was predicted by RNAfold while the HNADOCK was used for molecular docking analysis and specific binding of siRNAs to the selected target. We have used and evaluated four siRNAs for cellular toxicity and determination of antiviral efficiency based on the Ct value of q-real-time PCR in Vero E6 cells.
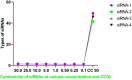
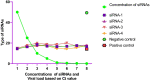
Results: Based on the experimental evaluation and analysis of results from generated data, we observed that there is no cytotoxicity for any tested siRNAs in Vero E6 cells. Total four siRNA were filtered out from twenty-one siRNAs following the strict selection and scoring criteria. The better antiviral efficiency was observed in 3rd siRNAs based on the Ct value of q-real-time PCR. The results that emerged from this study encouraged us to validate the efficiency of these siRNAs in multiple cells by using alone and in a combination of two or more siRNAs to inhibit the SARS-CoV-2 proliferation.
Conclusion: The Insilico prediction, molecular docking analysis provided the selection of better siRNAs. Based on the experimental evaluation only 3rd siRNA was found to be more effective than others and showed better antiviral efficiency. These siRNAs should also be evaluated in other cell lines either separately or in combination against SARS-CoV-2 to determine their antiviral efficiency.
Keywords: ARDS, Acute respiratory distress syndrome; COVID-19, The new Coronavirus Disease 2019; Insilico prediction; MFE, Minimum free energy; Molecular docking; PCR, Polymerase Chain Reaction; RBD, receptor binding domain; RNAi, RNA interference; SARS-CoV-2; SARS-CoV-2, Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2; Saudi Arabia; USFDA, United States Food and Drug Authority; Vero E6 cells; WHO, World Health Organization; siRNA, Short interfering RNA; siRNAs.
© 2022 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effect of insilico predicted and designed potential siRNAs on inhibition of SARS-CoV-2 in HEK-293 cells.J King Saud Univ Sci. 2022 Jun;34(4):101965. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2022.101965. Epub 2022 Mar 16. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2022. PMID: 35313445 Free PMC article.
-
In silico prediction and experimental validation of siRNAs targeting ORF1ab of MERS-CoV in Vero cell line.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021 Feb;28(2):1348-1355. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2020.11.066. Epub 2020 Nov 27. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33519276 Free PMC article.
-
Delivery of siRNAs against MERS-CoV in Vero and HEK-293 cells: A comparative evaluation of transfection reagents.J King Saud Univ Sci. 2023 Apr;35(3):102540. doi: 10.1016/j.jksus.2023.102540. Epub 2023 Jan 5. J King Saud Univ Sci. 2023. PMID: 36624781 Free PMC article.
-
Emergence, evolution, and vaccine production approaches of SARS-CoV-2 virus: Benefits of getting vaccinated and common questions.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):1981-1997. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.12.020. Epub 2021 Dec 13. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 34924802 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Current status of antivirals and druggable targets of SARS CoV-2 and other human pathogenic coronaviruses.Drug Resist Updat. 2020 Dec;53:100721. doi: 10.1016/j.drup.2020.100721. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Drug Resist Updat. 2020. PMID: 33132205 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico and In Vitro development of novel small interfering RNAs (siRNAs) to inhibit SARS-CoV-2.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025 Mar 23;27:1460-1471. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2025.03.034. eCollection 2025. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2025. PMID: 40256168 Free PMC article.
-
An ncRNA transcriptomics-based approach to design siRNA molecules against SARS-CoV-2 double membrane vesicle formation and accessory genes.BMC Infect Dis. 2023 Dec 12;23(1):872. doi: 10.1186/s12879-023-08870-0. BMC Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 38087193 Free PMC article.
-
Complement System Inhibitory Drugs in a Zebrafish (Danio rerio) Model: Computational Modeling.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 9;24(18):13895. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813895. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762197 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemistry-informed design selects potent siRNAs against SARS-CoV-2.RNA Biol. 2023 Jan;20(1):272-280. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2023.2217400. RNA Biol. 2023. PMID: 37272117 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alnylam Pharmaceuticals., 2020. Vir and Alnylam Expand Collaboration to Advance Rnai Therapeutics for the Treatment of Coronavirus Infection, Including Covid-19. Available online at: https://investors.alnylam.com/press-release?id= 24656.
-
- Alshukairi A.N., Tolah A.M., Dada A., Al-Tawfiq J.A., Almagharbi R.S., Saeedi M.F., Al-Hamzi M.A., El-Kafrawy S.A., Bahaudden H.A., El-Saed A., Al-Mozaini M.A., Khalid I., Hefni L.K., Hassan A.M., Alandijany T.A., Bajrai L.H., Bayumi D.T., Albishi G.E., Althawadi S.I., Zabani N.A., Perlman S., Azhar E.I. Test-based de-isolation in COVID-19 immunocompromised patients: Cycle threshold value versus SARS-CoV-2 viral culture. Internat. J. Infect. Diseases IJID. 2021;108:112–115. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azhar E.I., Hindawi S.I., El‐Kafrawy S.A., Hassan A.M., Tolah A.M., Alandijany T.A., Bajrai L.H., Damanhouri G.A. Amotosalen and ultraviolet A light treatment efficiently inactivates severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) in human plasma. Vox Sanguinis (December) 2020;116(6):673–681. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Azoulay E., Fartoukh M., Darmon M., Géri G., Voiriot G., Dupont T., Zafrani L., Girodias L., Labbé V., Dres M., Beurton A., Vieillard-Baron A., Demoule A. Increased mortality in patients with severe SARS-CoV-2 infection admitted within seven days of disease onset. Intensive Care Med. 2020;46(9):1714–1722. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
