Oncolytic Activity of a Chimeric Influenza A Virus Carrying a Human CTLA4 Antibody in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35494032
- PMCID: PMC9039307
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.875525
Oncolytic Activity of a Chimeric Influenza A Virus Carrying a Human CTLA4 Antibody in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
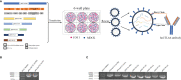
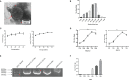
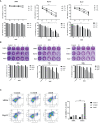
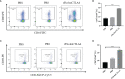
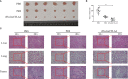
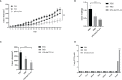
Oncolytic virotherapy belongs to a kind of active immunotherapy, which could trigger a potent antitumor immune response, showing great potential in clinical application. OVs could induce immune responses through the dual mechanisms of selective tumor killing without destroying normal tissues and induction of systemic antitumor immunity. In this study, we successfully rescued a chimeric oncolytic influenza virus carrying a human CTLA4 antibody in the background of the A/PR/8/34 (PR8) virus. The chimeric virus, called rFlu-huCTLA4, contained the heavy and light chains of the human CTLA4 antibody in the PB1 and PA segments of the PR8 virus, respectively. The first-generation hemagglutination (HA) titers of the rFlu-huCTLA4 virus ranged from 27 to 28, which could be passaged stably in specific pathogen-free (SPF) chicken embryos from P1 to P5. The morphology and size distribution of the chimeric virus were consistent with those of the wt influenza virus. The rFlu-huCTLA4 virus could effectively replicate in various cells in time- and dose-dependent manners. ELISA assay revealed that the secreted huCTLA4 antibody levels in chicken embryos increased gradually over time. Furthermore, MTS and crystal violet analysis showed that the selective cytotoxicity of the virus was higher in hepatocellular carcinoma cells (HepG2 and Huh7) than in normal liver cells (MIHA). In vivo experiments displayed that intratumoral injection with rFlu-huCTLA4 reduced tumor growth and increased the survival of mice compared with the PR8 group. More importantly, in the rFlu-huCTLA4 group, we found that CD4+ and CD8 +T cells were significantly increased in tumor-bearing BALB/c mice. Taken together, these findings demonstrated that the chimeric oncolytic virus rFlu-huCTLA4 could selectively destroy hepatocellular carcinoma cells in vitro and in vivo and may provide a promising clinical strategy for targeted immunotherapy of HCC with the oncolytic flu virus.
Keywords: CTLA4 antibody; HCC; generation hemagglutination; oncolytic virus; rFlu-huCTLA4.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Lei, Sun, Cheng, Yan, Zhang and Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

