Axillary Lymph Node Dissection Can Be Omitted in Breast Cancer Patients With Mastectomy and False-Negative Frozen Section in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
- PMID: 35494089
- PMCID: PMC9046780
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.869864
Axillary Lymph Node Dissection Can Be Omitted in Breast Cancer Patients With Mastectomy and False-Negative Frozen Section in Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Abstract
Background: The IBCSG 23-01 and AMAROS trials both reported that axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) did not change survival rates in breast cancer patients with positive nodes detected by sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB). The aim of this study was to determine whether breast cancer patients with mastectomy and false-negative frozen section (FS) in SLNB could forgo ALND.
Materials and methods: This was a retrospective study of cN0 patients diagnosed with primary invasive breast cancer treated by mastectomy and SLNB at our institute between January 2010 and December 2014. Patients with false-negative FS in SLNB were separated by the following management of axillary lymph node dissection in the non-ALND group (nonprocess or axillary radiation only) and ALND group (with or without radiation).
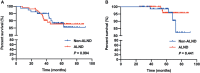
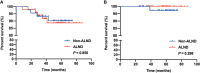
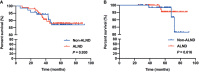
Results: A total of 212 patients were included, 86 and 126 patients in the non-ALND and ALND groups, respectively. The positive rate of non-sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) was 15.87% (20/126) in the ALND group. In multivariate analysis, we found that patients with larger tumor size (>2 cm) (OR, 1.989; p = 0.030) and multifocal lesions (OR, 3.542; p = 0.029) tended to receive ALND. The positivity of non-SLNs in the ALND group was associated with SLN macrometastasis (OR, 3.551; p = 0.043) and lymphovascular invasion (OR, 6.158; p = 0.003). Also, removing more SLNs (≥3) was related to negativity in non-SLNs (OR, 0.255; p = 0.016). After a median follow-up of 59.43 months, RFS and OS of the two groups were similar (p = 0.994 and 0.441). In subgroup analysis, we found that 97 patients who met the inclusive criteria of the IBCSG 23-01 trial had similar RFS and OS between the non-ALND and ALND groups (p = 0.856 and 0.298). The positive rate of non-SLNs was 9.62% (5/52). Also, in 174 patients who met the criteria of the AMAROS trial, RFS and OS in the non-ALND and ALND groups were similar (p = 0.930 and 0.616). The positive rate of non-SLNs was 18.27% (19/104).
Conclusion: ALND can be carefully omitted in selected breast cancer patients with mastectomy and false-negative FS in SLNB. SLNB is relatively sufficient in the IBCSG 23-01-eligible patients, and axillary radiation was an effective option in the AMAROS-eligible patients.
Keywords: axillary lymph node dissection; false-negative; frozen section; metastasis; sentinel lymph node biopsy.
Copyright © 2022 Si, Guo, Pan, Lu, Guo, Han, Xue, Xing, Wu and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Glechner A, Wockel A, Gartlehner G, Thaler K, Strobelberger M, Griebler U, et al. Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection Only Versus Complete Axillary Lymph Node Dissection in Early Invasive Breast Cancer: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Eur J Cancer (2013) 49:812–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2012.09.010 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous