Deep learning model for deep fake face recognition and detection
- PMID: 35494811
- PMCID: PMC9044351
- DOI: 10.7717/peerj-cs.881
Deep learning model for deep fake face recognition and detection
Abstract
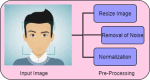
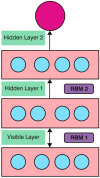
Deep Learning is an effective technique and used in various fields of natural language processing, computer vision, image processing and machine vision. Deep fakes uses deep learning technique to synthesis and manipulate image of a person in which human beings cannot distinguish the fake one. By using generative adversarial neural networks (GAN) deep fakes are generated which may threaten the public. Detecting deep fake image content plays a vital role. Many research works have been done in detection of deep fakes in image manipulation. The main issues in the existing techniques are inaccurate, consumption time is high. In this work we implement detecting of deep fake face image analysis using deep learning technique of fisherface using Local Binary Pattern Histogram (FF-LBPH). Fisherface algorithm is used to recognize the face by reduction of the dimension in the face space using LBPH. Then apply DBN with RBM for deep fake detection classifier. The public data sets used in this work are FFHQ, 100K-Faces DFFD, CASIA-WebFace.
Keywords: DBN; Deep fake; Deep learning; Fisherface; LBPH; RBM.
©2022 St et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare there are no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Afchar D, Nozick V, Yamagishi J, Echizen I. Mesonet: a compact facial video forgery detection network. 2018 IEEE international workshop on information forensics and security (WIFS); Piscataway. 2018. pp. 1–7.
-
- Allcott H, Gentzkow M. Social media and fake news in the 2016 election. Journal of economic perspectives. 2017;31(2):211–36. doi: 10.1257/jep.31.2.211. - DOI
-
- Arasaratnam I, Haykin S, Hurd TR. Cubature Kalman filtering for continuous-discrete systems: theory and simulations. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing. 2010;58(10):4977–4993. doi: 10.1109/TSP.2010.2056923. - DOI
-
- Arunkumar P, Kannimuthu S. Mining big data streams using business analytics tools: a birds eye view on moa and samoa. International Journal of Business Intelligence and Data Mining. 2020;17(2):226–236.
-
- Badale A, Castelino L, Darekar C, Gomes J. Deep fake detection using neural networks. 15th IEEE international conference on advanced video and signal based surveillance (AVSS); Piscataway. 2018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources