Functionalization of C-H bonds in acetophenone oximes with arylacetic acids and elemental sulfur
- PMID: 35495317
- PMCID: PMC9050572
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra00808g
Functionalization of C-H bonds in acetophenone oximes with arylacetic acids and elemental sulfur
Abstract
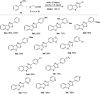
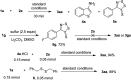
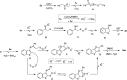
Fused thieno[3,2-d]thiazoles were synthesized via a coupling of acetophenone ketoximes, arylacetic acids, and elemental sulfur in the presence of Li2CO3 base. Functionalities including chloro, bromo, fluoro, trifluoromethyl, and pyridyl groups were compatible with reaction conditions. High yields and excellent regioselectivities were obtained even if meta-substituted ketoxime acetates were used. Ethyl esters of heteroarylacetic acids were competent substrates, which is very rare in the literature. Our method would offer a convenient protocol to afford polyheterocyclic structures from simple substrates.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


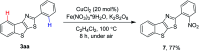
Similar articles
-
Homo- and Heteroannulation of sp3 C-H Bonds in Acetophenones for Divergent Synthesis of Thienothiazoles.Org Lett. 2019 Nov 1;21(21):8795-8799. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.9b03414. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Org Lett. 2019. PMID: 31644301
-
NH4I-promoted oxidative formation of benzothiazoles and thiazoles from arylacetic acids and phenylalanines with elemental sulfur.Org Biomol Chem. 2021 Jun 16;19(23):5108-5113. doi: 10.1039/d1ob00671a. Org Biomol Chem. 2021. PMID: 34009226
-
Copper-catalyzed [4+2] oxidative annulation of α,β-unsaturated ketoxime acetates with ethyl trifluoropyruvate.Chem Commun (Camb). 2022 Jun 9;58(47):6757-6760. doi: 10.1039/d2cc01573k. Chem Commun (Camb). 2022. PMID: 35611963
-
Unusual Formation of 1,2,4-Oxadiazine Core in Reaction of Amidoximes with Maleic or Fumaric Esters.Molecules. 2022 Nov 3;27(21):7508. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217508. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364335 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative trifluoromethylation and trifluoromethylthiolation reactions using (trifluoromethyl)trimethylsilane as a nucleophilic CF3 source.Acc Chem Res. 2014 May 20;47(5):1513-22. doi: 10.1021/ar4003202. Epub 2014 Apr 28. Acc Chem Res. 2014. PMID: 24773518 Review.
References
-
-
For selected examples, see:
- Kakiuchi F. Kan S. Igi K. Chatani N. Murai S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:1698. doi: 10.1021/ja029273f. - DOI - PubMed
- Kimura N. Kochi T. Kakiuchi F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017;139:14849. doi: 10.1021/jacs.7b08385. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhu R.-Y. Li Z.-Q. Park H. S. Senanayake C. H. Yu J.-Q. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018;140:3564. doi: 10.1021/jacs.8b01359. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Xing D. Qi X. Marchant D. Liu P. Dong G. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019;58:4366. doi: 10.1002/anie.201900301. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- St John-Campbell S. White A. J. P. Bull J. A. Chem. Sci. 2017;8:4840. doi: 10.1039/C7SC01218G. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Yao Q.-J. Zhang S. Zhan B.-B. Shi B.-F. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017;56:6617. doi: 10.1002/anie.201701849. - DOI - PubMed
- Li B. Seth K. Niu B. Pan L. Yang H. Ge H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018;57:3401. doi: 10.1002/anie.201713357. - DOI - PubMed
- Chen X.-Y. Sorensen E. J. Chem. Sci. 2018;9:8951. doi: 10.1039/C8SC03606C. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Xu W. Yoshikai N. Org. Lett. 2018;20:1392. doi: 10.1021/acs.orglett.8b00164. - DOI - PubMed
- Hu Y. Zhou B. Chen H. Wang C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2018;57:12071. doi: 10.1002/anie.201806287. - DOI - PubMed
-
-
-
For review, see:
- Huang H. Ji X. Wu W. Jiang H. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015;44:1155. doi: 10.1039/C4CS00288A. - DOI - PubMed
-
Selected examples:
- Desai L. V. Malik H. A. Sanford M. S. Org. Lett. 2006;8:1141. doi: 10.1021/ol0530272. - DOI - PubMed
- Neely J. M. Rovis T. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:66. doi: 10.1021/ja3104389. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Ye B. Cramer N. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014;53:7896. doi: 10.1002/anie.201404895. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhang H. Wang K. Wang B. Yi H. Hu F. Li C. Zhang Y. Wang J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2014;53:13234. doi: 10.1002/anie.201408555. - DOI - PubMed
- Sun B. Yoshino T. Kanai M. Matsunaga S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2015;54:12968. doi: 10.1002/anie.201507744. - DOI - PubMed
- Li Y. Chen H. Qu L.-B. Houk K. N. Lan Y. ACS Catal. 2019;9:7154. doi: 10.1021/acscatal.9b02085. - DOI
-
-
- Liu S. Liebeskind L. S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008;130:6918. doi: 10.1021/ja8013743. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Ren Z.-H. Zhang Z.-Y. Yang B.-Q. Wang Y. Y. Guan Z.-H. Org. Lett. 2011;13:5394. doi: 10.1021/ol202290y. - DOI - PubMed
- Wei Y. Yoshikai N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013;135:3756. doi: 10.1021/ja312346s. - DOI - PubMed
- Huang H. Cai J. Ji X. Xiao F. Chen Y. Deng G.-J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2016;55:307. doi: 10.1002/anie.201508076. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhu C. Zhu R. Zeng H. Chen F. Liu C. Wu W. Jiang H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2017;56:13324. doi: 10.1002/anie.201707719. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhu Z. Tang X. Cen J. Li J. Wu W. Jiang H. Chem. Commun. 2018;54:3767. doi: 10.1039/C8CC00445E. - DOI - PubMed
-
-
Selected examples:
- Lutz J. P. Hannigan M. D. McNeil A. J. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018;376:225. doi: 10.1016/j.ccr.2018.07.015. - DOI
- Nakanishi I. Itoh S. Suenobu T. Fukuzumi S. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1998;37:992. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1521-3773(19980420)37:7<992::AID-ANIE992>3.0.CO;2-P. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhang C. Zhu X. Acc. Chem. Res. 2017;50:1342. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00050. - DOI - PubMed
- Cinar M. E. Ozturk T. Chem. Rev. 2015;115:3036. doi: 10.1021/cr500271a. - DOI - PubMed
-
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

