A case of empyema necessitans in an adolescent with mycobacterium tuberculosis
- PMID: 35495393
- PMCID: PMC9052272
- DOI: 10.1016/j.amsu.2022.103540
A case of empyema necessitans in an adolescent with mycobacterium tuberculosis
Abstract
Introduction and importance: An empyema is a buildup of pus in the pleural space and is most commonly associated with pneumonia. Streptococcus pneumonia is the most common cause of pneumonia, although staphylococcus aureus is common in developing countries. empyema necsitans is An extravasation of purulent material outside the pleural space involving the chest wall.
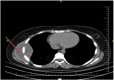
Case presentation: Here we present a 15-year-old girl presented with swelling on the right thorax wall. I was told that the swelling had been there for 1 year with moderate discomfort upon lifting objects, with no other complaints. Her medical history was unremarkable until the mass appeared. There was no history of fever, cough, or weight loss, and there was no family history of tuberculosis.
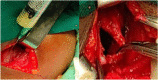
Clinical discussion: Empyema necessitatis can be quite harmful. It has the potential to cause bone and soft tissue erosion. This may be asymptomatic at first and proceed at a slow and steady pace. Tuberculous EN can be treated with both surgical and medical treatments. This case applies to both surgical intervention and medical treatment with antituberculosis.
Conclusion: Empyema necessitans is uncommon consequence of pleural space infection. pulmonary mycobacterium tuberculosis, Actinomyces, and nontuberculous organisms such Staphylococcus aureus are the most prevalent causes.
Keywords: Chest wall mass; Empyema necesitans; Tuberculosis.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bhanja S., Guha A., Samanta A., Mia H.A., Kumar N. A Case of Empyema necessitans: an uncommon presentation of Empyema. Int. J. Pediatr. 2017;5(7):5351–5355.
-
- Acar M., Sutcu M., Akturk H.G., Topyildiz E., Somer A., Erol O.B., Erkose Genc G., Salman N. A case of empyema necessitatis in a child with Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Clin. Pediatr. 2016 Oct;55(12):1165–1167. - PubMed
-
- Moore F.O., Berne J.D., McGovern T.M., Ravishankar S., Slamon N.B., Hertzog J.H. Empyema necessitatis in an infant: a rare surgical disease. J. Pediatr. Surg. 2006 Jul 1;41(7):e5–7. - PubMed
-
- Agha R.A., Franchi T., Sohrabi C., Mathew G., Kerwan A., Thoma A., Beamish A.J., Noureldin A., Rao A., Vasudevan B., Challacombe B. The SCARE 2020 guideline: updating consensus surgical CAse REport (SCARE) guidelines. Int. J. Surg. 2020 Dec 1;84:226–230. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials