Catalysis with magnetically retrievable and recyclable nanoparticles layered with Pd(0) for C-C/C-O coupling in water
- PMID: 35495980
- PMCID: PMC9049700
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra10618a
Catalysis with magnetically retrievable and recyclable nanoparticles layered with Pd(0) for C-C/C-O coupling in water
Abstract
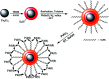
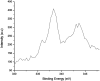
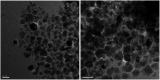
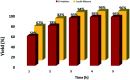
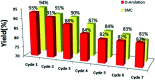
Nanoparticles layered with palladium(0) were prepared from nano-sized magnetic Fe3O4 by coating it with silica and then reacting sequentially with phenylselenyl chloride under an N2 atmosphere and palladium(ii) chloride in water. The resulting Fe3O4@SiO2@SePh@Pd(0) NPs are magnetically retrievable and the first example of NPs in which the outermost layer of Pd(0) is mainly held by selenium. The weight percentage of Pd in the NPs was found to be 1.96 by ICP-AES. The NPs were authenticated via TEM, SEM-EDX, XPS, and powder XRD and found to be efficient as catalysts for the C-O and C-C (Suzuki-Miyaura) coupling reactions of ArBr/Cl in water. The oxidation state of Pd in the NPs having size distribution from ∼12 to 18 nm was inferred as zero by XPS. They can be recycled more than seven times. The main features of the proposed protocols are their mild reaction conditions, simplicity, and efficiency as the catalyst can be separated easily from the reaction mixture by an external magnet and reused for a new reaction cycle. The optimum loading (in mol% of Pd) was found to be 0.1-1.0 and 0.01-1.0 for O-arylation and Suzuki-Miyaura coupling, respectively. For ArCl, the required amount of NPs was more as compared to that needed for ArBr. The nature of catalysis is largely heterogeneous.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Rafiee E. Eavani S. Green Chem. 2011;13:2116. doi: 10.1039/C1GC15291B. - DOI
- Dálaigh C. Ó. Corr S. A. Gun’ko Y. Connon S. J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2007;46:4329. doi: 10.1002/anie.200605216. - DOI - PubMed
- Lai D. M. Deng L. Li J. Liao B. Guo Q. X. Fu Y. ChemSusChem. 2011;4:55. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201000300. - DOI - PubMed
- Zhang Y. Xia C. G. Appl. Catal., A. 2009;366:141. doi: 10.1016/j.apcata.2009.06.041. - DOI
- Zheng X. X. Luo S. Z. Zhang L. Cheng J. P. Green Chem. 2009;11:455. doi: 10.1039/B823123K. - DOI
-
- Polshettiwar V. Varma R. S. Green Chem. 2010;12:743. doi: 10.1039/B921171C. - DOI
-
- Abu-Reziq R. Alper H. Wang D. S. Post M. L. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006;128:5279. doi: 10.1021/ja060140u. - DOI - PubMed
- Chouhan G. Wang D. S. Alper H. Chem. Commun. 2007:4809. doi: 10.1039/B711298J. - DOI - PubMed
- Hara T. Kaneta T. Mori K. Mitsudome T. Mizugaki T. Ebitani K. Kaneda K. Green Chem. 2007;9:1246. doi: 10.1039/B704912A. - DOI
- Jin M. J. Lee D. H. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2010;49:1119. doi: 10.1002/anie.200905626. - DOI - PubMed
- Yang H. Q. Wang Y. Qin Y. Chong Y. Yang Q. Li G. Zhang L. Li W. Green Chem. 2011;13:1352. doi: 10.1039/C0GC00955E. - DOI
- Garca-Garrido S. E. Francos J. Cadierno V. Basset J.-M. Polshettiwar V. ChemSusChem. 2011;4:104. doi: 10.1002/cssc.201000280. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

