Social Achievement Goals in Chinese Undergraduates: Associations With Self-Esteem and Symptoms of Social Anxiety and Depression
- PMID: 35496191
- PMCID: PMC9043354
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.726679
Social Achievement Goals in Chinese Undergraduates: Associations With Self-Esteem and Symptoms of Social Anxiety and Depression
Abstract
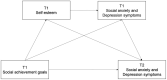
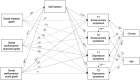
The pursuit of relationship goals is critical to the wellbeing of young adults. This study investigated different achievement goals toward social competence as potential predictors of social anxiety and depression symptoms. It proposed that self-esteem may function as a mediator on the pathway from endorsing social achievement goals to undergraduates' concurrent and longitudinal social anxiety and depression symptoms. Social achievement goal theory proposes three types of goals: social mastery goals (striving to improve one's social competence), social performance-approach goals (striving to prove one's social competence and win positive evaluation), and social performance-avoid goals (striving to avoid incompetent social behaviors and negative evaluation). One hundred and eighty-five Chinese undergraduates aged from 18 to 23 (50% female) completed this study across two-time points. Path analyses indicated that social mastery (marginally) and performance-approach goals were positively associated with self-esteem, whereas social performance-avoid goals were negatively associated with self-esteem; self-esteem was negatively associated with the concurrent social anxiety and depression symptoms and the longitudinal depression symptoms. The proposed mediation effects of self-esteem on the links from three types of social achievement goals to the concurrent and longitudinal social anxiety and depression symptoms were significant except on the links from social mastery goals and social performance-approach goals to the subsequent social anxiety symptoms. Self-esteem and the baseline social anxiety and depressive symptoms have a chain mediating effect between social achievement goals and the longitudinal symptoms of social anxiety and depression. These findings suggest that the pursuit of social mastery goals and performance-approach goals in initiating and maintaining social relationships boosts undergraduates' self-worth and reduces their concurrent and longitudinal depression experiences. However, the strivings to hide inadequacy and avoid negative evaluation in social contexts impede one's self-worth and increase concurrent and longitudinal social anxiety and depression symptoms. Implications and limitations are discussed.
Keywords: depression symptoms; self-esteem; social achievement goals; social anxiety symptoms; undergraduates.
Copyright © 2022 Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Achievement motivation and mental health among medical postgraduates: the chain mediating effect of self-esteem and perceived stress.Front Psychol. 2024 Oct 23;15:1483090. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1483090. eCollection 2024. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 39507085 Free PMC article.
-
The relationship between social achievement goals and self-esteem, depression and anxiety among medical school students.Niger J Clin Pract. 2023 Sep;26(9):1335-1341. doi: 10.4103/njcp.njcp_69_23. Niger J Clin Pract. 2023. PMID: 37794547
-
Achievement Goals as Mediators of the Links Between Self-Esteem and Depressive Symptoms From Mid-Adolescence to Early Adulthood.J Youth Adolesc. 2025 Jan;54(1):103-120. doi: 10.1007/s10964-024-02045-z. Epub 2024 Jul 4. J Youth Adolesc. 2025. PMID: 38963580
-
The pursuit of self-esteem: contingencies of self-worth and self-regulation.J Pers. 2006 Dec;74(6):1749-71. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-6494.2006.00427.x. J Pers. 2006. PMID: 17083665 Review.
-
Unmasking artifactual links: A reanalysis reveals No direct causal relationship between self-esteem and quality of social relations.Heliyon. 2023 Sep 22;9(10):e20397. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e20397. eCollection 2023 Oct. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37767502 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Unraveling the core symptoms of mental health in senior grade three students- a network analysis.Front Psychiatry. 2024 Apr 22;15:1364334. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1364334. eCollection 2024. Front Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 38711876 Free PMC article.
-
Cumulative childhood trauma and cybervictimization among Chinese college students: Internet addiction as a mediator and roommate relationships as a moderator.Front Psychol. 2022 Aug 17;13:791291. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.791291. eCollection 2022. Front Psychol. 2022. PMID: 36092086 Free PMC article.
-
Association between physical activity and adolescent mental health in the post COVID-19: The chain mediating effect of self-esteem and social anxiety.PLoS One. 2024 May 17;19(5):e0301617. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0301617. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38758776 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bardach L., Graf D., Yanagida T., Kollmayer M., Spiel C., Lüftenegger M. (2020). Gendered pathways to bullying perpetration via social achievement goals – mediating effects of sense of belonging and non-inclusive group norms. J. Sch. Violence 19, 248–263. 10.1080/15388220.2019.1660883 - DOI
-
- Beck A. T.. (1967). Depression: Clinical, Experimental, and Theoretical Aspects. New York, NY: Harper & Row.
-
- Bongers K. C. A., Dijksterhuis A., Spears R. (2009). Self-esteem regulation after success and failure to attain unconsciously activated goals. J. Exp. Soc. Psychol. 45, 468–477. 10.1016/j.jesp.2008.12.007 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous