Urinary Profile of Endogenous Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid and its Biomarker Metabolites in Healthy Korean Females: Determination of Age-Dependent and Intra-Individual Variability and Identification of Metabolites Correlated With Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid
- PMID: 35496306
- PMCID: PMC9043528
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.853971
Urinary Profile of Endogenous Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid and its Biomarker Metabolites in Healthy Korean Females: Determination of Age-Dependent and Intra-Individual Variability and Identification of Metabolites Correlated With Gamma-Hydroxybutyric Acid
Abstract
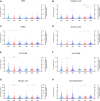
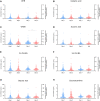
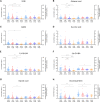
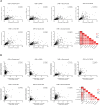
Gamma-hydroxybutyric acid (GHB), used as a therapeutic and an illegal anesthetic, is a human neurotransmitter produced during gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) biosynthesis and metabolism. Potential biomarker metabolites of GHB intoxication have been identified previously; however, reference concentrations have not been set due to the lack of clinical study data. Urinary profiling of endogenous GHB and its biomarker metabolites in urine samples (n = 472) of 206 healthy females was performed based on differences in age and time of sample collection using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry following validation studies. The unadjusted and creatinine-adjusted urinary concentrations ranges were obtained after urinary profiling. The creatinine-adjusted concentrations of glutamic and succinic acids and succinylcarnitine significantly increased, whereas that of glycolic acid significantly decreased with advancing age. Significant inter-day variation of GABA concentration and intra-day variation of 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid and succinylcarnitine concentrations were observed. The urinary concentrations of 2,4-dihydroxybutyric acid, succinic acid, and 3,4-dihydroxybutyric acid showed the highest correlation with that of GHB. Data from this study suggest population reference limits to facilitate clinical and forensic decisions related to GHB intoxication and could be useful for identification of biomarkers following comparison with urinary profiles of GHB-administered populations.
Keywords: biomarker metabolites; gamma-hydroxybutyric acid; liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry; metabolite profiling; urine.
Copyright © 2022 Kim, Choi, Lee, Kim, Park, Han, Han, Lee and Lee.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

