Quantification of unperturbed phosphoprotein levels in immune cell subsets with phosphoflow to assess immune signaling in autoimmune disease
- PMID: 35496781
- PMCID: PMC9038771
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101309
Quantification of unperturbed phosphoprotein levels in immune cell subsets with phosphoflow to assess immune signaling in autoimmune disease
Abstract
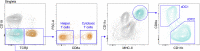
Activation of innate immune sensors by endogenous DNA and RNA can lead to autoimmune and autoinflammatory diseases. Quantification of the unperturbed phosphoprotein content in immune cells provides insight into the spontaneous activity of immune signaling pathways triggered by nucleic acid recognition. Here, we present a phosphoflow protocol for measuring phosphoproteins in mouse models of autoimmunity that incorporates strategies to preserve native phosphoprotein levels during sample collection and to reliably detect low signaling activity common in chronic disease states. For complete details on the use and execution of this protocol, please refer to Jütte et al. (2021).
Keywords: Flow Cytometry/Mass Cytometry; Immunology.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Hulspas R., O’Gorman M.R.G., Wood B.L., Gratama J.W., Sutherland D.R. Considerations for the control of background fluorescence in clinical flow cytometry. Cytometry. 2009;76B:355–364. - PubMed
-
- Krutzik P.O., Nolan G.P. Intracellular phospho-protein staining techniques for flow cytometry: monitoring single cell signaling events. Cytometry. 2003;55A:61–70. - PubMed
-
- Maecker H.T., Trotter J. Flow cytometry controls, instrument setup, and the determination of positivity. Cytometry. 2006;69A:1037–1042. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

