Comparative genome analysis of the first Listeria monocytogenes core genome multi-locus sequence types CT2050 AND CT2051 strains with their close relatives
- PMID: 35496987
- PMCID: PMC8995181
- DOI: 10.3934/microbiol.2022006
Comparative genome analysis of the first Listeria monocytogenes core genome multi-locus sequence types CT2050 AND CT2051 strains with their close relatives
Abstract
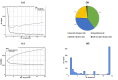
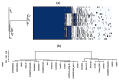
Genome sequences of the three strains of L. monocytogenes, which are the first core genome multi-locus sequence types (cgMLST) 2050 and 2051 were reviewed and compared with 21 close relatives and reference genomes. Using a pan-genomic approach to analyse whole genome sequences, it was found that the strains consisted of approximately 2200 shared genes and a much greater pool of genes present as an accessory genome. An unknown transmissible sequence of approximately 91 kb harbouring bacitracin resistance genes found in strain LmNG2 (1/2b) was revealed to be an Inc18 plasmid. The CT2051, strain LmNG3 (1/2a) haboured more unique genes (252 vs 230) than the well-known reference strain LmEGD-e (1/2a). More studies to monitor new strains can help reduce food-borne outbreaks.
Keywords: Listeria monocytogenes; antimicrobial resistance genes; bacitracin genes; genomics; pan-genome; plasmid.
© 2022 the Author(s), licensee AIMS Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kallipolitis B, Gahan CGM, Piveteau P. Factors contributing to Listeria monocytogenes transmission and impact on food safety. Curr Opin Food Sci. 2020;36:9–17. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2020.09.009. - DOI
-
- Nwaiwu O. Molecular serotype and evolutionary lineage of Listeria monocytogenes isolated from different Nigerian food items. Afr J Biotechnol. 2016;15:696–705. doi: 10.5897/AJB2015.15125. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
