Role of vitamin C in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity
- PMID: 35496992
- PMCID: PMC8995185
- DOI: 10.3934/microbiol.2022010
Role of vitamin C in preventing of COVID-19 infection, progression and severity
Abstract
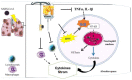
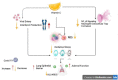
Vitamin C stands as an essential water-soluble vitamin, antioxidant and has been shown to enhance immunity. SARS-CoV-2 has been spreading rapidly across the worldwide, several cellular processes of innate and adaptive immunity are aided by vitamin C, which strengthens the immune system overall. Multiple lines of evidence in the literature associate vitamin C with antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticoagulant and immunomodulatory actions. Pneumonia and sepsis patients had poor ascorbic acid status and high oxidative stress, according to many studies. Pneumonia patients who get vitamin C may have less severe symptoms and a longer course of the illness if they do. To standardize plasma levels in sepsis patients, gram measurements of the vitamin must be administered intravenously (IV). This intervention has been shown in a few trials to reduce mortality. COVID-19 management in China and the United States has exhibited remarkable results when using a high percentage of intravenous vitamins C. It's acceptable to include vitamin C in the COVID-19 treatment protocol as a secondary measure based on the current active clinical studies looking at the impact of vitamin C on the management of COVID-19. Patients with hypovitaminosis C or severe respiratory illnesses, such as COVID-19, may benefit from taking vitamin C, due to its good safety profile, simplicity of use, and potential for rapid production scaling. The study's goal was to see whether high dosage intravenous vitamin C had any impact on individuals with severe COVID-19 (HDIVC). Finally we discuss recent research that has been published on the efficacy of vitamin C administration in the treatment of viral infection and life-threatening conditions. The purpose of this manuscript is to summarise existing research on the efficacy of vitamin C as a treatment for COVID-19 and to discuss possible explanations for why it may work in some individuals but not in others.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-oxidant; antiviral; sepsis; vitamin C.
© 2022 the Author(s), licensee AIMS Press.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
