Paper-Based Devices for Capturing Exosomes and Exosomal Nucleic Acids From Biological Samples
- PMID: 35497368
- PMCID: PMC9039228
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.836082
Paper-Based Devices for Capturing Exosomes and Exosomal Nucleic Acids From Biological Samples
Abstract
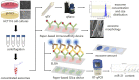
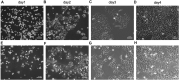
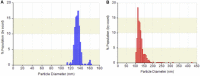
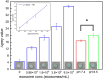
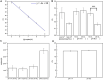
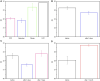
Exosomes, nanovesicles derived from cells, contain a variety of biomolecules that can be considered biomarkers for disease diagnosis, including microRNAs (miRNAs). Given knowledge and demand, inexpensive, robust, and easy-to-use tools that are compatible with downstream nucleic acid detection should be developed to replace traditional methodologies for point-of-care testing (POCT) applications. This study deploys a paper-based extraction kit for exosome and exosomal miRNA analytical system with some quantifying methods to serve as an easy sample preparation for a possible POCT process. Exosomes concentrated from HCT116 cell cultures were arrested on paper-based immunoaffinity devices, which were produced by immobilizing anti-CD63 antibodies on Whatman filter paper, before being subjected to paper-based silica devices for nucleic acids to be trapped by silica nanoparticles adsorbed onto Whatman filter paper. Concentrations of captured exosomes were quantified by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA), demonstrating that paper-based immunoaffinity devices succeeded in capturing and determining exosome levels from cells cultured in both neutral and acidic microenvironments, whereas microRNA 21 (miR-21), a biomarker for various types of cancers and among the nucleic acids absorbed onto the silica devices, was determined by reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) to prove that paper-based silica devices were capable of trapping exosomal nucleic acids. The developed paper-based kit and the devised procedure was successfully exploited to isolate exosomes and exosomal nucleic acids from different biological samples (platelet-poor plasma and lesion fluid) as clinical applications.
Keywords: colorimetric sensing; exosomal miRNA; exosome; immunoassay; nucleic acid extraction; paper-based device; plasma; wound fluid.
Copyright © 2022 Lai, Lee, Vu, Vu, Tsai, Chen and Cheng.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Intermittent lysis on a single paper-based device to extract exosomal nucleic acid biomarkers from biological samples for downstream analysis.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Aug 2;191(8):501. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06566-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39093424
-
Paper/PMMA hybrid device with a microvalve-controlled design for exosome isolation and analysis.Talanta. 2023 Dec 1;265:124851. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2023.124851. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Talanta. 2023. PMID: 37354627
-
Subpopulations of exosomes purified via different exosomal markers carry different microRNA contents.Int J Med Sci. 2021 Jan 1;18(4):1058-1066. doi: 10.7150/ijms.52768. eCollection 2021. Int J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33456364 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomal microRNA panels as biomarkers for hematological malignancies.Curr Probl Cancer. 2021 Oct;45(5):100726. doi: 10.1016/j.currproblcancer.2021.100726. Epub 2021 Mar 5. Curr Probl Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33752898 Review.
-
Exosomal miRNAs as novel cancer biomarkers: Challenges and opportunities.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Sep;233(9):6370-6380. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26481. Epub 2018 Mar 25. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29323722 Review.
Cited by
-
Intermittent lysis on a single paper-based device to extract exosomal nucleic acid biomarkers from biological samples for downstream analysis.Mikrochim Acta. 2024 Aug 2;191(8):501. doi: 10.1007/s00604-024-06566-z. Mikrochim Acta. 2024. PMID: 39093424
-
Paper-Based Exosomal MicroRNA-21 Detection for Wound Monitoring: A Proof of Concept and Clinical Validation Trial Study.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 6;24(12):9822. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129822. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37372974 Free PMC article.
-
The new advance of exosome-based liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 8;22(1):610. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02863-0. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39380060 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bautista-Sánchez D., Arriaga-Canon C., Pedroza-Torres A., De La Rosa-Velázquez I. A., González-Barrios R., Contreras-Espinosa L., et al. (2020). The Promising Role of miR-21 as a Cancer Biomarker and its Importance in RNA-Based Therapeutics. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 20, 409–420. 10.1016/j.omtn.2020.03.003 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

