Poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate- co-ethylene dimethacrylate]nanogel by dispersion polymerization for inhibition of pathogenic bacteria
- PMID: 35497568
- PMCID: PMC9042309
- DOI: 10.1039/d1ra06231j
Poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate- co-ethylene dimethacrylate]nanogel by dispersion polymerization for inhibition of pathogenic bacteria
Abstract
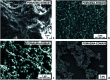
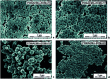
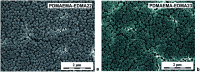
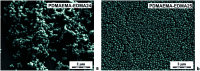
Bacterial infections and antimicrobial resistance are one of the major public health problems and various strategies to prevent potential threats have been developed. Protonated polymers were proven as efficient agents against several microbial pathogens. Poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate] (PDMAEMA) linear polymer and its copolymers represent one example of functional materials which inhibit the growth of both harmful Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria. However, the antimicrobial effect of positively charged PDMAEMA particles has been never tested. In this report, we deeply studied several parameters of free-radical polymerization, including the effect of crosslinking monomer, medium composition, solvency and polarity, and type and concentration of initiator and stabilizer, to fabricate high-quality poly[2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate-co-ethylene dimethacrylate] (PDMAEMA-EDMA) nanogel. We successfully found that dispersion polymerization in water/2-methoxyethanol medium (80/20 w/w), initiated with 0.2 wt% potassium persulfate (KPS) and stabilized with 0.5 wt% poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA), produced a well-defined and sub-micron 167 nm PDMAEMA-EDMA nanogel. Bactericidal activity of the quaternized PDMAEMA-EDMA nanogel was assessed via time-kill curve assay against two Gram-positive and Gram-negative pathogenic bacteria, namely Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) and Acinetobacter baumannii (A. baumannii). The results illustrated that the quaternized PDMAEMA-EDMA nanogel acted as an effective bactericidal agent against both tested bacteria.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures

References
-
- Voorn D. J. Ming W. van Herk A. M. Macromolecules. 2005;38:3653–3662. doi: 10.1021/ma0475030. - DOI
-
- Natu A. M. Wiggins M. van de Mark M. R. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2015;293:1191–1204. doi: 10.1007/s00396-015-3508-9. - DOI
-
- Liu Q. Li Y. Duan Y. Zhou H. Polym. Int. 2012;61:1593–1602. doi: 10.1002/pi.4347. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

