Simulation of Mechanical Heart Valve Dysfunction and the Non-Newtonian Blood Model Approach
- PMID: 35498142
- PMCID: PMC9042627
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/9612296
Simulation of Mechanical Heart Valve Dysfunction and the Non-Newtonian Blood Model Approach
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Simulation of Mechanical Heart Valve Dysfunction and the Non-Newtonian Blood Model Approach.Appl Bionics Biomech. 2023 Nov 29;2023:9896350. doi: 10.1155/2023/9896350. eCollection 2023. Appl Bionics Biomech. 2023. PMID: 38075140 Free PMC article.
Abstract
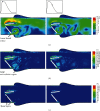
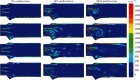
The mechanical heart valve (MHV) is commonly used for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases. Nonphysiological hemodynamic in the MHV may cause hemolysis, platelet activation, and an increased risk of thromboembolism. Thromboembolism may cause severe complications and valve dysfunction. This paper thoroughly reviewed the simulation of physical quantities (velocity distribution, vortex formation, and shear stress) in healthy and dysfunctional MHV and reviewed the non-Newtonian blood flow characteristics in MHV. In the MHV numerical study, the dysfunction will affect the simulation results, increase the pressure gradient and shear stress, and change the blood flow patterns, increasing the risks of hemolysis and platelet activation. The blood flow passes downstream and has obvious recirculation and stagnation region with the increased dysfunction severity. Due to the complex structure of the MHV, the non-Newtonian shear-thinning viscosity blood characteristics become apparent in MHV simulations. The comparative study between Newtonian and non-Newtonian always shows the difference. The shear-thinning blood viscosity model is the basics to build the blood, also the blood exhibiting viscoelastic properties. More details are needed to establish a complete and more realistic simulation.
Copyright © 2022 Aolin Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared that they have no conflicts of interest regarding this work.
Figures
References
-
- Zhengwan Z. H. A. N. G., Chunjiong Z. H. A. N. G., Hongbing L. I., Tao X. I. E. Multipath transmission selection algorithm based on immune connectivity model. Journal of Computer Applications . 2020;40(12):p. 3571.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

