Electronic system for step width estimation using programmable system-on-chip technology and time of flight cameras
- PMID: 35498248
- PMCID: PMC9041237
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ohx.2020.e00126
Electronic system for step width estimation using programmable system-on-chip technology and time of flight cameras
Abstract
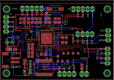
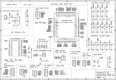
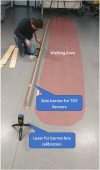
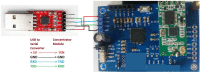
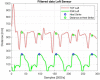
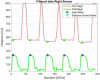
This paper proposes a low-cost portable electronic system for estimating step width during the human gait cycle. This device, intended to support the Walking Stance item of the fall risk assessment test Performance Oriented Mobility Assessment (POMA), contains three electronic boards, comprising two sensing nodes and a concentrator. Each sensing node contains a force sensitive resistor (FSR) and time-of-flight camera (TOF). Each FSR is placed inside the subject's shoe, while each TOF camera is located at the back of their foot. The FSR detects contact between heel and ground, and the TOF measures the distance to a barrier located on the right side of the walking path. Step width is calculated as the difference between the TOF measurements. After the walk is complete, the information obtained by the FSRs and TOFs is sent via a 433 MHz wireless communication to the concentrator board, which is connected to the USB port of a personal computer (PC). The proposed step width measurement system was validated with an infrared based motion capture (Vicon Corp.), giving an error equal to 11.4% 5.5%.
Keywords: Human gait; Motion capture; POMA test; Programming system on chip; Step width; Time-of-flight camera.
© 2020 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures








References
-
- Tinetti M.E. Performance-Oriented Assessment of Mobility Problems in Elderly Patients. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 1986;34(2):119–126. - PubMed
-
- Nordin E., Moe-Nilssen R., Ramnemark A., Lundin-Olsson L. Changes in step-width during dual-task walking predicts falls. Gait Posture. 2010;32(1):92–97. - PubMed
-
- Silva J., Sousa I. IEEE International Symposium on Medical Measurements and Applications (MeMeA) 2016. Instrumented Timed Up and Go : Fall Risk Assessment based on Inertial Wearable Sensors; pp. 1–6.
-
- Doheny E.P., Fan C.W., Foran T., Greene B.R., Cunningham C., Kenny R.A. Proceedings of the Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society. 2011. “An instrumented sit-to-stand test used to examine differences between older fallers and non-fallers”, in; pp. 3063–3066. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

