Merits of photocatalytic and antimicrobial applications of gamma-irradiated Co x Ni1- x Fe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9 nanocomposite for pyridine removal and pathogenic bacteria/fungi disinfection: implication for wastewater treatment
- PMID: 35498317
- PMCID: PMC9049020
- DOI: 10.1039/c9ra10505k
Merits of photocatalytic and antimicrobial applications of gamma-irradiated Co x Ni1- x Fe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9 nanocomposite for pyridine removal and pathogenic bacteria/fungi disinfection: implication for wastewater treatment
Abstract
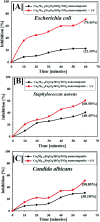
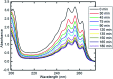
In this paper, we report a layer-by-layer approach for the preparation of a concentric recyclable composite (Co x Ni1-x Fe2O4/SiO2/TiO2; x = 0.9) designed for wastewater treatment. The prepared composite was investigated by X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, high-resolution transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy (SEM) supported with energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) spectroscopy to analyze crystallinity, average particle size, morphology and elemental composition, respectively. The antimicrobial activities of the prepared composite have been investigated against multi-drug-resistant bacteria and pathogenic fungi using a variety of experiments, such as zone of inhibition, minimum inhibitory concentration, biofilm formation and SEM with EDX analysis of the treated bacterial cells. In addition, the effects of gamma irradiation (with different doses) and UV irradiation on the antibacterial abilities of the prepared composite have been evaluated. Moreover, the effect of gamma irradiation on the crystallite size of the prepared composite has been studied under varying doses of radiation (25 kGy, 50 kGy and 100 kGy). Finally, the photocatalytic efficiency of the prepared composite was tested for halogen-lamp-assisted removal of pyridine (artificial wastewater). Various parameters affecting the efficiency of the photocatalytic degradation, such as photocatalyst dose, pyridine concentration, pH, point of zero charge and the presence of hydrogen peroxide, have been studied. Our results show that the synthesized composite has a well-crystallized semi-spherical morphology with an average particle size of 125.84 nm. In addition, it possesses a high degree of purity, as revealed by EDX elemental analysis. Interestingly, the prepared composite showed promising antibacterial abilities against almost all the tested pathogenic bacteria and unicellular fungi, and this was further improved after gamma and UV irradiation. Finally, the prepared composite was very efficient in the light-assisted degradation of pyridine and its degradation efficiency can be tuned based on various experimental parameters. This work provides a revolutionary nanomaterial-based solution for the global water shortage and water contamination by offering a new wastewater treatment technique that is recyclable, cost effective and has an acceptable time and quality of water.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures














References
-
- Hill E. DiSalvo R. Environmental Epidemiology. 2019;3:159.
-
- Nath B. Resonance. 2019;24:575–582. doi: 10.1007/s12045-019-0811-7. - DOI
-
- Forde M., Izurieta R. and Ôrmeci B., Water Quality in the Americas, 2019, vol. 27
-
- Ritter P. I. and Sanchez R., Prenatal Exposure to Acute Diarrheal Diseases and Childhood Mortality, 2019
-
- Ravindra K. Mor S. Pinnaka V. L. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019:1–11. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

