Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Expressed by the Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells Dictates Thymus Involution in Murine Pregnancy
- PMID: 35498436
- PMCID: PMC9046655
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.846226
Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Expressed by the Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells Dictates Thymus Involution in Murine Pregnancy
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Nuclear Progesterone Receptor Expressed by the Cortical Thymic Epithelial Cells Dictates Thymus Involution in Murine Pregnancy.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 21;13:958735. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.958735. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35800431 Free PMC article.
Abstract
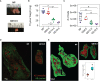
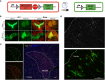
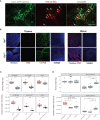
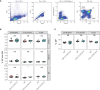
Progesterone is a gonadal pro-gestational hormone that is absolutely necessary for the success of pregnancy. Most notable actions of progesterone are observed in the female reproductive organs, the uterus and the ovary. Acting through the nuclear progesterone receptor (PGR), progesterone prepares the endometrium for implantation of the embryo. Interestingly, the maternal thymus also is a known expressor of Pgr; its absence is associated with murine pregnancy complications. However, the localization of its expression and its functional importance were not known. Here, we used a transgenic dual fluorescent reporter mouse model and genetic deletion of Pgr in Foxn1+ thymic epithelial cells (TEC) to demonstrate TEC-specific Pgr expression in pregnancy, especially in the cortex where thymocyte maturation occurs. Using our TEC-specific Pgr deletion mouse model, we demonstrate that TEC-specific Pgr is necessary for pregnancy-induced thymic involution in pregnancy. Our investigation reveals that PGR expression is upregulated in the cortical thymic epithelial cells during pregnancy, and that PGR expression is important for thymic involution during murine pregnancy.
Keywords: fertility; involution; pregnancy; progesterone receptor (PGR); thymus.
Copyright © 2022 Ahn, Nguyen, Kim, Jeong, Arora, Lydon and Petroff.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer S-PW declared a past collaboration with two of the authors JL and J-WJ to the handling editor.
Figures



References
-
- Moore TA, von Freeden-Jeffry U, Murray R, Zlotnik A. Inhibition of Gamma Delta T Cell Development and Early Thymocyte Maturation in IL-7 -/- Mice. J Immunol (1996) 157:2366–73. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

