A Meta-Analysis of Biostimulant Yield Effectiveness in Field Trials
- PMID: 35498677
- PMCID: PMC9047501
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.836702
A Meta-Analysis of Biostimulant Yield Effectiveness in Field Trials
Abstract
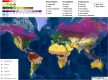
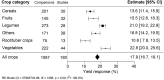
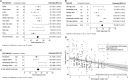
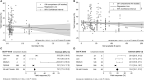
Today's agriculture faces many concerns in maintaining crop yield while adapting to climate change and transitioning to more sustainable cultivation practices. The application of plant biostimulants (PBs) is one of the methods that step forward to address these challenges. The advantages of PBs have been reported numerous times. Yet, there is a general lack of quantitative assessment of the overall impact of PBs on crop production. Here we report a comprehensive meta-analysis on biostimulants (focus on non-microbial PBs) of over one thousand pairs of open-field data in a total of 180 qualified studies worldwide. Yield gains in open-field cultivation upon biostimulant application were compared across different parameters: biostimulant category, application method, crop species, climate condition, and soil property. The overall results showed that (1) the add-on yield benefit among all biostimulant categories is on average 17.9% and reached the highest potential via soil treatment; (2) biostimulant applied in arid climates and vegetable cultivation had the highest impact on crop yield; and (3) biostimulants were more efficient in low soil organic matter content, non-neutral, saline, nutrient-insufficient, and sandy soils. This systematic review provides general biostimulant application guidelines and gives consultants and growers insights into achieving an optimal benefit from biostimulant application.
Keywords: biostimulant; climate; crop yield; meta-analysis; open-field trial; soil quality; sustainable agriculture.
Copyright © 2022 Li, Van Gerrewey and Geelen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmad B., Zaid A., Sadiq Y., Bashir S., Wani S.H. (2019). Role of selective exogenous elicitors in plant responses to abiotic stress tolerance. Plant Abiotic Stress Tolerance 273–290. 10.1007/978-3-030-06118-0_12 - DOI
-
- Bayu T. (2020). Review on contribution of integrated soil fertility management for climate change mitigation and agricultural sustainability. Cogent Environ. Sci. 6, 1823631. 10.1080/23311843.2020.1823631 - DOI
-
- Bio4Safe I.S.P. (2021). Biostimulant Database. Available online at: https://bio4safe.eu/ (accessed March 10, 2022).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

