Induction of ADCC by a folic acid-mAb conjugate prepared by tryptophan-selective reaction toward folate-receptor-positive cancer cells
- PMID: 35498849
- PMCID: PMC9053046
- DOI: 10.1039/d0ra03291c
Induction of ADCC by a folic acid-mAb conjugate prepared by tryptophan-selective reaction toward folate-receptor-positive cancer cells
Abstract
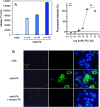
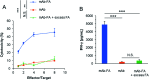
We developed conjugates between monoclonal antibody (mAb) and folic acid (FA) by using a tryptophan (Trp)-selective reaction, which yields relatively homogenous products compared to conventional methods. The obtained mAb-FA conjugates showed significant cellular cytotoxicity toward folate receptor-expressing cancer cells, demonstrating that the conjugates retained the Fc region's original function.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures



References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

