The unmet need of evidence-based therapy for patients with advanced chronic kidney disease and heart failure: Position paper from the Cardiorenal Working Groups of the Spanish Society of Nephrology and the Spanish Society of Cardiology
- PMID: 35498889
- PMCID: PMC9050562
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfab290
The unmet need of evidence-based therapy for patients with advanced chronic kidney disease and heart failure: Position paper from the Cardiorenal Working Groups of the Spanish Society of Nephrology and the Spanish Society of Cardiology
Abstract
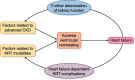
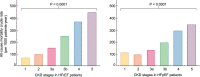
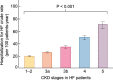
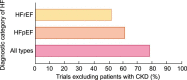
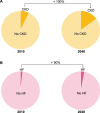
Despite the high prevalence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) and its high cardiovascular risk, patients with CKD, especially those with advanced CKD (stages 4-5 and patients on kidney replacement therapy), are excluded from most cardiovascular clinical trials. It is particularly relevant in patients with advanced CKD and heart failure (HF) who have been underrepresented in many pivotal randomized trials that have modified the management of HF. For this reason, there is little or no direct evidence for HF therapies in patients with advanced CKD and treatment is extrapolated from patients without CKD or patients with earlier CKD stages. The major consequence of the lack of direct evidence is the under-prescription of HF drugs to this patient population. As patients with advanced CKD and HF represent probably the highest cardiovascular risk population, the exclusion of these patients from HF trials is a serious deontological fault that must be solved. There is an urgent need to generate evidence on how to treat HF in patients with advanced CKD. This article briefly reviews the management challenges posed by HF in patients with CKD and proposes a road map to address them.
Keywords: advanced chronic kidney disease; heart failure; kidney failure; kidney replacement therapy.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the ERA.
Figures
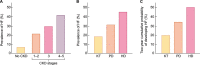
Similar articles
-
Characteristics of Patients with Heart Failure and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease (Stages 4-5) Not Undergoing Renal Replacement Therapy (ERCA-IC Study).J Clin Med. 2023 Mar 17;12(6):2339. doi: 10.3390/jcm12062339. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36983339 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between β-Blocker Use and Mortality/Morbidity in Patients With Heart Failure With Reduced, Midrange, and Preserved Ejection Fraction and Advanced Chronic Kidney Disease.Circ Heart Fail. 2020 Nov;13(11):e007180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCHEARTFAILURE.120.007180. Epub 2020 Oct 19. Circ Heart Fail. 2020. PMID: 33070637
-
Burden and challenges of heart failure in patients with chronic kidney disease. A call to action.Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2020 May-Jun;40(3):223-236. doi: 10.1016/j.nefro.2019.10.005. Epub 2019 Dec 31. Nefrologia (Engl Ed). 2020. PMID: 31901373 Review. English, Spanish.
-
Long-term impact of cardiorenal syndromes on major outcomes based on their chronology: a comprehensive French nationwide cohort study.Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022 Nov 23;37(12):2386-2397. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfac153. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2022. PMID: 35438794
-
Management of Heart Failure in Advancing CKD: Core Curriculum 2018.Am J Kidney Dis. 2018 Aug;72(2):284-295. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2017.12.006. Epub 2018 Feb 23. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018. PMID: 29478868 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenine model of chronic renal failure in rats to determine whether MCC950, an NLRP3 inflammasome inhibitor, is a renopreventive.BMC Nephrol. 2023 Dec 19;24(1):377. doi: 10.1186/s12882-023-03427-4. BMC Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 38114914 Free PMC article.
-
Characteristics and outcome of hospitalized patients with heart failure stratified for chronic kidney disease.ESC Heart Fail. 2024 Oct;11(5):3341-3349. doi: 10.1002/ehf2.14827. Epub 2024 Jul 4. ESC Heart Fail. 2024. PMID: 38965818 Free PMC article.
-
Practical approaches to building up a cardiorenal clinic.Clin Kidney J. 2022 Dec 7;16(5):780-792. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfac258. eCollection 2023 May. Clin Kidney J. 2022. PMID: 37151411 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The effect of kidney function on guideline-directed medical therapy implementation and prognosis in heart failure with reduced ejection fraction.Clin Cardiol. 2024 Feb;47(2):e24244. doi: 10.1002/clc.24244. Clin Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38402552 Free PMC article.
-
Survival differences according to baseline characteristics of patient with advanced heart failure treated with levosimendan.SAGE Open Med. 2025 Jul 17;13:20503121251357357. doi: 10.1177/20503121251357357. eCollection 2025. SAGE Open Med. 2025. PMID: 40689263 Free PMC article.
References
-
- van der Velde M, Matsushita K, Coresh Jet al. . Lower estimated glomerular filtration rate and higher albuminuria are associated with all-cause and cardiovascular mortality. A collaborative meta-analysis of high-risk population cohorts. Kidney Int 2011; 79: 1341–1352 - PubMed
-
- Gansevoort RT, Correa-Rotter R, Hemmelgarn BRet al. . Chronic kidney disease and cardiovascular risk: epidemiology, mechanisms, and prevention. Lancet 2013; 382: 339–352 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

