Effects of Ilisha elongata proteins on proliferation and adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum
- PMID: 35499024
- PMCID: PMC9039923
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100206
Effects of Ilisha elongata proteins on proliferation and adhesion of Lactobacillus plantarum
Abstract
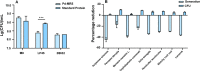
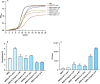
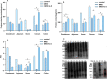
The effects of aquatic proteins on the proliferation and adhesion of intestinal probiotic bacteria were investigated by in vitro fermentation and mouse in vitrointestinal tissue models. Compared with the control group, the Illisha elongata protein reduced the growth time of Lactobacillus plantarum (LP45) by 34.25% and increased the total number of colonies by 6.61%. The Ilisha elongata salt-solubale protein performed better than water-soluble protein in vitro proliferation of LP45. Ilisha elongata salt-soluble protein significantly increased the number of viable bacteria adhering to intestinal, and caused changes in the amount of polysaccharides, proteins and biofilms in the intestinal tissue model. These results indicate that the Ilisha elongata protein is beneficial to the proliferation and adhesion of probiotics in the intestinal, and can be used as an active protein beneficial to intestinal health.
Keywords: Adhesion; Ilisha elongata proteins; Lactobacillus plantarum; Proliferation.
© 2022 Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Zhang Y.-C., Zhang L.-W., Tuo Y.-F., Guo C.-F., Yi H.-X., Li J.-Y., et al. Inhibition of shigella sonnei adherence to ht-29 cells by lactobacilli from chinese fermented food and preliminary characterization of s-layer protein involvement. Research in Microbiology. 2010;161(8):667–672. - PubMed
-
- Baarlen P.V., Troost F.J., Hemert S.V., Meer C.V.D., Vos W.M.D., Groot P.J.D., et al. Differential nf-κb pathways induction by lactobacillus plantarum in the duodenum of healthy humans correlating with immune tolerance. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(7):2371–2376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0809919106. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

