Angioregulatory microRNAs in breast cancer : Molecular mechanistic basis and implications for therapeutic strategies
- PMID: 35499045
- PMCID: PMC9039675
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jare.2021.06.019
Angioregulatory microRNAs in breast cancer : Molecular mechanistic basis and implications for therapeutic strategies
Abstract
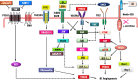
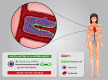
Background: Cancer-associated angiogenesis is a fundamental process in tumor growth and metastasis. A variety of signaling regulators and pathways contribute to establish neovascularization, among them as small endogenous non-coding RNAs, microRNAs (miRNAs) play prominent dual regulatory function in breast cancer (BC) angiogenesis.
Aim of review: This review aims at describing the current state-of-the-art in BC angiogenesis-mediated by angioregulatory miRNAs, and an overview of miRNAs dysregulation association with the anti-angiogenic response in addition to potential clinical application of miRNAs-based therapeutics.
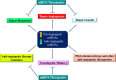
Key scientific concepts of review: Angioregulatory miRNA-target gene interaction is not only involved in sprouting vessels of breast tumors but also, trans-differentiation of BC cells to endothelial cells (ECs) in a process termed vasculogenic mimicry. Using canonical and non-canonical angiogenesis pathways, the tumor cell employs the oncogenic characteristics such as miRNAs dysregulation to increase survival, proliferation, oxygen and nutrient supply, and treatment resistance. Angioregulatory miRNAs in BC cells and their microenvironment have therapeutic potential in cancer treatment. Although, miRNAs dysregulation can serve as tumor biomarker nevertheless, due to the association of miRNAs dysregulation with anti-angiogenic resistant phenotype, clinical benefits of anti-angiogenic therapy might be challenging in BC. Hence, unveiling the molecular mechanism underlying angioregulatory miRNAs sparked a booming interest in finding new treatment strategies such as miRNA-based therapies in BC.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Angioregulatory microRNA; Anti-angiogenic therapeutics; Breast cancer; Vascular mimicry.
© 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier B.V. on behalf of Cairo University.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures






References
-
- Li Y.J., Wen G., Wang Y., Wang D.X., Yang L., Deng Y.J., et al. Perfusion heterogeneity in breast tumors for assessment of angiogenesis. J Ultrasound Med: Off J Am Inst Ultrasound Med. 2013;32(7):1145–1155. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

