At the Crux of Joint Crosstalk: TGFβ Signaling in the Synovial Joint
- PMID: 35499698
- PMCID: PMC9184360
- DOI: 10.1007/s11926-022-01074-6
At the Crux of Joint Crosstalk: TGFβ Signaling in the Synovial Joint
Abstract
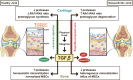
Purpose of review: The effect of the transforming growth factor beta (TGFβ) signaling pathway on joint homeostasis is tissue-specific, non-linear, and context-dependent, representing a unique complexity in targeting TGFβ signaling in joint disease. Here we discuss the variety of mechanisms that TGFβ signaling employs in the synovial joint to maintain healthy joint crosstalk and the ways in which aberrant TGFβ signaling can result in joint degeneration.
Recent findings: Osteoarthritis (OA) epitomizes a condition of disordered joint crosstalk in which multiple joint tissues degenerate leading to overall joint deterioration. Synovial joint tissues, such as subchondral bone, articular cartilage, and synovium, as well as mesenchymal stem cells, each demonstrate aberrant TGFβ signaling during joint disease, whether by excessive or suppressed signaling, imbalance of canonical and non-canonical signaling, a perturbed mechanical microenvironment, or a distorted response to TGFβ signaling during aging. The synovial joint relies upon a sophisticated alliance among each joint tissue to maintain joint homeostasis. The TGFβ signaling pathway is a key regulator of the health of individual joint tissues, and the subsequent interaction among these different joint tissues, also known as joint crosstalk. Dissecting the sophisticated function of TGFβ signaling in the synovial joint is key to therapeutically interrogating the pathway to optimize overall joint health.
Keywords: Articular cartilage; Joint crosstalk; Osteoarthritis; Subchondral bone; TGF beta.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

