An iterative algorithm for optimizing COVID-19 vaccination strategies considering unknown supply
- PMID: 35499997
- PMCID: PMC9060336
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0265957
An iterative algorithm for optimizing COVID-19 vaccination strategies considering unknown supply
Abstract
Background and objective: The distribution of the newly developed vaccines presents a great challenge in the ongoing SARS-CoV-2 pandemic. Policy makers must decide which subgroups should be vaccinated first to minimize the negative consequences of the pandemic. These decisions must be made upfront and under uncertainty regarding the amount of vaccine doses available at a given time. The objective of the present work was to develop an iterative optimization algorithm, which provides a prioritization order of predefined subgroups. The results of this algorithm should be optimal but also robust with respect to potentially limited vaccine supply.
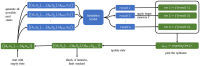
Methods: We present an optimization meta-heuristic which can be used in a classic simulation-optimization setting with a simulation model in a feedback loop. The meta-heuristic can be applied in combination with any epidemiological simulation model capable of depicting the effects of vaccine distribution to the modeled population, accepts a vaccine prioritization plan in a certain notation as input, and generates decision making relevant variables such as COVID-19 caused deaths or hospitalizations as output. We finally demonstrate the mechanics of the algorithm presenting the results of a case study performed with an epidemiological agent-based model.
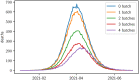
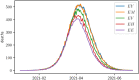
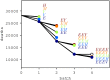
Results: We show that the developed method generates a highly robust vaccination prioritization plan which is proven to fulfill an elegant supremacy criterion: the plan is equally optimal for any quantity of vaccine doses available. The algorithm was tested on a case study in the Austrian context and it generated a vaccination plan prioritization favoring individuals age 65+, followed by vulnerable groups, to minimize COVID-19 related burden.
Discussion: The results of the case study coincide with the international policy recommendations which strengthen the applicability of the approach. We conclude that the path-dependent optimum optimum provided by the algorithm is well suited for real world applications, in which decision makers need to develop strategies upfront under high levels of uncertainty.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Technical guidelines for seasonal influenza vaccination in China (2021-2022)].Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2021 Oct 10;42(10):1722-1749. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112338-20210913-00732. Zhonghua Liu Xing Bing Xue Za Zhi. 2021. PMID: 34814607 Chinese.
-
Estimated Number of COVID-19 Infections, Hospitalizations, and Deaths Prevented Among Vaccinated Persons in the US, December 2020 to September 2021.JAMA Netw Open. 2022 Jul 1;5(7):e2220385. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.20385. JAMA Netw Open. 2022. PMID: 35793085 Free PMC article.
-
[Technical guidelines for seasonal influenza vaccination in China (2022-2023)].Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022 Oct 6;56(10):1356-1386. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112150-20220825-00840. Zhonghua Yu Fang Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36274602 Chinese.
-
Beneficial effects of SARS-CoV-2 vaccination resulting from the COVID-19 pandemic with regard to the uptake of influenza virus, pneumococcal, and herpes zoster adult vaccination - a narrative literature review.Ann Agric Environ Med. 2023 Dec 22;30(4):587-594. doi: 10.26444/aaem/176747. Epub 2023 Dec 20. Ann Agric Environ Med. 2023. PMID: 38153058 Review.
-
Determinants of Influenza Vaccine Uptake in Patients With Cardiovascular Disease and Strategies for Improvement.J Am Heart Assoc. 2021 Aug 3;10(15):e019671. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.120.019671. Epub 2021 Jul 28. J Am Heart Assoc. 2021. PMID: 34315229 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

