The anterior Hox gene ceh-13 and elt-1/GATA activate the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 to specify posterior lineages in the C. elegans embryo
- PMID: 35500030
- PMCID: PMC9098060
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1010187
The anterior Hox gene ceh-13 and elt-1/GATA activate the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 to specify posterior lineages in the C. elegans embryo
Abstract
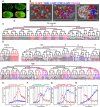
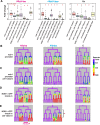
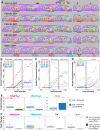
Hox transcription factors play a conserved role in specifying positional identity during animal development, with posterior Hox genes typically repressing the expression of more anterior Hox genes. Here, we dissect the regulation of the posterior Hox genes nob-1 and php-3 in the nematode C. elegans. We show that nob-1 and php-3 are co-expressed in gastrulation-stage embryos in cells that previously expressed the anterior Hox gene ceh-13. This expression is controlled by several partially redundant transcriptional enhancers. These enhancers act in a ceh-13-dependant manner, providing a striking example of an anterior Hox gene positively regulating a posterior Hox gene. Several other regulators also act positively through nob-1/php-3 enhancers, including elt-1/GATA, ceh-20/ceh-40/Pbx, unc-62/Meis, pop-1/TCF, ceh-36/Otx, and unc-30/Pitx. We identified defects in both cell position and cell division patterns in ceh-13 and nob-1;php-3 mutants, suggesting that these factors regulate lineage identity in addition to positional identity. Together, our results highlight the complexity and flexibility of Hox gene regulation and function and the ability of developmental transcription factors to regulate different targets in different stages of development.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Roles of the Homothorax/Meis/Prep homolog UNC-62 and the Exd/Pbx homologs CEH-20 and CEH-40 in C. elegans embryogenesis.Development. 2002 Nov;129(22):5255-68. doi: 10.1242/dev.129.22.5255. Development. 2002. PMID: 12399316
-
Anterior organization of the Caenorhabditis elegans embryo by the labial-like Hox gene ceh-13.Development. 1999 Apr;126(7):1537-46. doi: 10.1242/dev.126.7.1537. Development. 1999. PMID: 10068646
-
The roles of two C. elegans HOX co-factor orthologs in cell migration and vulva development.Development. 2005 Mar;132(6):1413-28. doi: 10.1242/dev.01569. Development. 2005. PMID: 15750187
-
The Caenorhabditis elegans intestine.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013 May-Jun;2(3):347-67. doi: 10.1002/wdev.93. Epub 2012 Oct 9. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23799580 Review.
-
Hox gene functions in the C. elegans nervous system: From early patterning to maintenance of neuronal identity.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Jan-Feb;152-153:58-69. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2022.11.012. Epub 2022 Dec 7. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 36496326 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neurogenesis in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2024 Oct 7;228(2):iyae116. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyae116. Genetics. 2024. PMID: 39167071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A molecular atlas of adult C. elegans motor neurons reveals ancient diversity delineated by conserved transcription factor codes.Cell Rep. 2024 Mar 26;43(3):113857. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.113857. Epub 2024 Feb 29. Cell Rep. 2024. PMID: 38421866 Free PMC article.
-
Partial coupling of the proliferation and differentiation programs during C. elegans intestine development.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 Jul 30:2024.04.07.588410. doi: 10.1101/2024.04.07.588410. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40766359 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
pop-1/TCF, ref-2/ZIC and T-box factors regulate the development of anterior cells in the C. elegans embryo.Dev Biol. 2022 Sep;489:34-46. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2022.05.019. Epub 2022 May 31. Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35660370 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanisms of lineage specification in Caenorhabditis elegans.Genetics. 2023 Dec 6;225(4):iyad174. doi: 10.1093/genetics/iyad174. Genetics. 2023. PMID: 37847877 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Duboule D, Morata G. Colinearity and functional hierarchy among genes of the homeotic complexes. Trends Genet TIG. 1994. Oct;10(10):358–64. - PubMed
-
- Noordermeer D, Duboule D. Chromatin architectures and Hox gene collinearity. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2013;104:113–48. - PubMed
-
- Gaunt SJ. Hox cluster genes and collinearities throughout the tree of animal life. Int J Dev Biol. 2018;62(11–12):673–83. - PubMed
-
- Bürglin TR, Ruvkun G, Coulson A, Hawkins NC, McGhee JD, Schaller D, et al.. Nematode homeobox cluster. Nature. 1991. Jun 27;351(6329):703. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

