Spiropyrimidinetrione DNA Gyrase Inhibitors with Potent and Selective Antituberculosis Activity
- PMID: 35500229
- PMCID: PMC9233935
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.2c00266
Spiropyrimidinetrione DNA Gyrase Inhibitors with Potent and Selective Antituberculosis Activity
Abstract
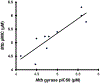
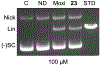
New antibiotics with either a novel mode of action or novel mode of inhibition are urgently needed to overcome the threat of drug-resistant tuberculosis (TB). The present study profiles new spiropyrimidinetriones (SPTs), DNA gyrase inhibitors having activity against drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb), the causative agent of TB. While the clinical candidate zoliflodacin has progressed to phase 3 trials for the treatment of gonorrhea, compounds herein demonstrated higher inhibitory potency against Mtb DNA gyrase (e.g., compound 42 with IC50 = 2.0) and lower Mtb minimum inhibitor concentrations (0.49 μM for 42). Notably, 42 and analogues showed selective Mtb activity relative to representative Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. DNA gyrase inhibition was shown to involve stabilization of double-cleaved DNA, while on-target activity was supported by hypersensitivity against a gyrA hypomorph. Finally, a docking model for SPTs with Mtb DNA gyrase was developed, and a structural hypothesis was built for structure-activity relationship expansion.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures


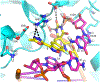



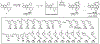
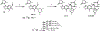
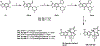

References
-
- Tuberculosis: Key facts. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (accessed February 14, 2022).
-
- New TB drugs. https://tbfacts.org/new-tb-drugs/ (accessed February 14, 2022).
-
- Bandodkar B; Shandil RK; Bhat J; Balganesh TS, Two decades of TB drug discovery efforts—what have we learned? Applied Sciences 2020, 10, 5704.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

