The Association between Serum Lipids and Intraocular Pressure in 2 Large United Kingdom Cohorts
- PMID: 35500606
- PMCID: PMC10444694
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2022.04.023
The Association between Serum Lipids and Intraocular Pressure in 2 Large United Kingdom Cohorts
Abstract
Purpose: Serum lipids are modifiable, routinely collected blood test features associated with cardiovascular health. We examined the association of commonly collected serum lipid measures (total cholesterol [TC], high-density lipoprotein cholesterol [HDL-C], low-density lipoprotein cholesterol [LDL-C], and triglycerides) with intraocular pressure (IOP).
Design: Cross-sectional study in the UK Biobank and European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC)-Norfolk cohorts.
Participants: We included 94 323 participants from the UK Biobank (mean age, 57 years) and 6230 participants from the EPIC-Norfolk (mean age, 68 years) cohorts with data on TC, HDL-C, LDL-C, and triglycerides collected between 2006 and 2009.
Methods: Multivariate linear regression adjusting for demographic, lifestyle, anthropometric, medical, and ophthalmic covariables was used to examine the associations of serum lipids with corneal-compensated IOP (IOPcc).
Main outcome measures: Corneal-compensated IOP.
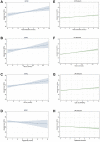
Results: Higher levels of TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C were associated independently with higher IOPcc in both cohorts after adjustment for key demographic, medical, and lifestyle factors. For each 1-standard deviation increase in TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C, IOPcc was higher by 0.09 mmHg (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.06-0.11 mmHg; P < 0.001), 0.11 mmHg (95% CI, 0.08-0.13 mmHg; P < 0.001), and 0.07 mmHg (95% CI, 0.05-0.09 mmHg; P < 0.001), respectively, in the UK Biobank cohort. In the EPIC-Norfolk cohort, each 1-standard deviation increase in TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C was associated with a higher IOPcc by 0.19 mmHg (95% CI, 0.07-0.31 mmHg; P = 0.001), 0.14 mmHg (95% CI, 0.03-0.25 mmHg; P = 0.016), and 0.17 mmHg (95% CI, 0.06-0.29 mmHg; P = 0.003). An inverse association between triglyceride levels and IOP in the UK Biobank (-0.05 mmHg; 95% CI, -0.08 to -0.03; P < 0.001) was not replicated in the EPIC-Norfolk cohort (P = 0.30).
Conclusions: Our findings suggest that serum TC, HDL-C, and LDL-C are associated positively with IOP in 2 United Kingdom cohorts and that triglyceride levels may be associated negatively. Future research is required to assess whether these associations are causal in nature.
Keywords: Cholesterol; Glaucoma; Intraocular pressure; Lipids.
Copyright © 2022 American Academy of Ophthalmology. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Stein J.D., Khawaja A.P., Weizer J.S. Glaucoma in adults—screening, diagnosis, and management: a review. JAMA. 2021;325(2):164–174. - PubMed
-
- Klein B.E., Klein R. Intraocular pressure and cardiovascular risk variables. Arch Ophthalmol. 1981;99(5):837–839. - PubMed
-
- Mori K., Ando F., Nomura H., et al. Relationship between intraocular pressure and obesity in Japan. Int J Epidemiol. 2000;29(4):661–666. - PubMed
-
- Lee A., Rochtchina E., Wang J.J., et al. Does smoking affect intraocular pressure? Findings from the Blue Mountains Eye Study. J Glaucoma. 2003;12(3):209–212. - PubMed
-
- Wang S., Bao X. Hyperlipidemia, blood lipid level, and the risk of glaucoma: a meta-analysis. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2019;60(4):1028–1043. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MR/T019050/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/T040912/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MC_QA137853/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- C864/A8257/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G1000143/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- MR/N003284/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- G0401527/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EY015473/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- MC_PC_17228/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 EY032559/EY/NEI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- 220558/Z/20/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- SP2024/0201/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 14136/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- G9502233/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom

