Pathogenic variants of Valosin-containing protein induce lysosomal damage and transcriptional activation of autophagy regulators in neuronal cells
- PMID: 35501124
- PMCID: PMC10588520
- DOI: 10.1111/nan.12818
Pathogenic variants of Valosin-containing protein induce lysosomal damage and transcriptional activation of autophagy regulators in neuronal cells
Abstract
Aim: Mutations in the valosin-containing protein (VCP) gene cause various lethal proteinopathies that mainly include inclusion body myopathy with Paget's disease of bone and frontotemporal dementia (IBMPFD) and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS). Different pathological mechanisms have been proposed. Here, we define the impact of VCP mutants on lysosomes and how cellular homeostasis is restored by inducing autophagy in the presence of lysosomal damage.
Methods: By electron microscopy, we studied lysosomal morphology in VCP animal and motoneuronal models. With the use of western blotting, real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR), immunofluorescence and filter trap assay, we evaluated the effect of selected VCP mutants in neuronal cells on lysosome size and activity, lysosomal membrane permeabilization and their impact on autophagy.
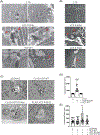
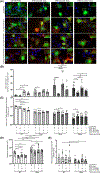
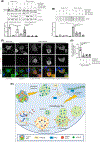
Results: We found that VCP mutants induce the formation of aberrant multilamellar organelles in VCP animal and cell models similar to those found in patients with VCP mutations or with lysosomal storage disorders. In neuronal cells, we found altered lysosomal activity characterised by membrane permeabilization with galectin-3 redistribution and activation of PPP3CB. This selectively activated the autophagy/lysosomal transcriptional regulator TFE3, but not TFEB, and enhanced both SQSTM1/p62 and lipidated MAP1LC3B levels inducing autophagy. Moreover, we found that wild type VCP, but not the mutants, counteracted lysosomal damage induced either by trehalose or by a mutant form of SOD1 (G93A), also blocking the formation of its insoluble intracellular aggregates. Thus, chronic activation of autophagy might fuel the formation of multilamellar bodies.
Conclusion: Together, our findings provide insights into the pathogenesis of VCP-related diseases, by proposing a novel mechanism of multilamellar body formation induced by VCP mutants that involves lysosomal damage and induction of lysophagy.
Keywords: ALS; PQC; TFE3; lysosome; neurodegeneration; p97.
© 2022 The Authors. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of British Neuropathological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





Similar articles
-
VCP maintains lysosomal homeostasis and TFEB activity in differentiated skeletal muscle.Autophagy. 2019 Jun;15(6):1082-1099. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2019.1569933. Epub 2019 Jan 29. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30654731 Free PMC article.
-
Trehalose induces autophagy via lysosomal-mediated TFEB activation in models of motoneuron degeneration.Autophagy. 2019 Apr;15(4):631-651. doi: 10.1080/15548627.2018.1535292. Epub 2018 Nov 5. Autophagy. 2019. PMID: 30335591 Free PMC article.
-
IBMPFD Disease-Causing Mutant VCP/p97 Proteins Are Targets of Autophagic-Lysosomal Degradation.PLoS One. 2016 Oct 21;11(10):e0164864. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0164864. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27768726 Free PMC article.
-
Valosin-Containing Protein (VCP)/p97 Oligomerization.Subcell Biochem. 2024;104:485-501. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-58843-3_18. Subcell Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38963497 Review.
-
The multiple faces of valosin-containing protein-associated diseases: inclusion body myopathy with Paget's disease of bone, frontotemporal dementia, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.J Mol Neurosci. 2011 Nov;45(3):522-31. doi: 10.1007/s12031-011-9627-y. Epub 2011 Sep 3. J Mol Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21892620 Review.
Cited by
-
Underlying Mechanism of Lysosomal Membrane Permeabilization in CNS Injury: A Literature Review.Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Jan;62(1):626-642. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04290-6. Epub 2024 Jun 18. Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 38888836 Review.
-
Cardiac-Specific Suppression of Valosin-Containing Protein Induces Progressive Heart Failure and Premature Mortality Correlating with Temporal Dysregulations in mTOR Complex 2 and Protein Phosphatase 1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 11;25(12):6445. doi: 10.3390/ijms25126445. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38928151 Free PMC article.
-
ALS-related p97 R155H mutation disrupts lysophagy in iPSC-derived motor neurons.Stem Cell Reports. 2024 Mar 12;19(3):366-382. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2024.01.002. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Stem Cell Reports. 2024. PMID: 38335961 Free PMC article.
-
Elamipretide alleviates pyroptosis in traumatically injured spinal cord by inhibiting cPLA2-induced lysosomal membrane permeabilization.J Neuroinflammation. 2023 Jan 7;20(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12974-023-02690-4. J Neuroinflammation. 2023. PMID: 36609266 Free PMC article.
-
Valosin containing protein (VCP): initiator, modifier, and potential drug target for neurodegenerative diseases.Mol Neurodegener. 2023 Aug 7;18(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13024-023-00639-y. Mol Neurodegener. 2023. PMID: 37545006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

