The pathological role of damaged organelles in renal tubular epithelial cells in the progression of acute kidney injury
- PMID: 35501332
- PMCID: PMC9061711
- DOI: 10.1038/s41420-022-01034-0
The pathological role of damaged organelles in renal tubular epithelial cells in the progression of acute kidney injury
Abstract
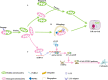
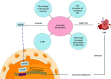
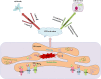
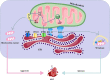
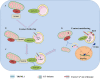
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a common clinical condition associated with high morbidity and mortality. The pathogenesis of AKI has not been fully elucidated, with a lack of effective treatment. Renal tubular epithelial cells (TECs) play an important role in AKI, and their damage and repair largely determine the progression and prognosis of AKI. In recent decades, it has been found that the mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum (ER), lysosomes, and other organelles in TECs are damaged to varying degrees in AKI, and that they can influence each other through various signaling mechanisms that affect the recovery of TECs. However, the association between these multifaceted signaling platforms, particularly between mitochondria and lysosomes during AKI remains unclear. This review summarizes the specific pathophysiological mechanisms of the main TECs organelles in the context of AKI, particularly the potential interactions among them, in order to provide insights into possible novel treatment strategies.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

