Multi-omics single-cell data integration and regulatory inference with graph-linked embedding
- PMID: 35501393
- PMCID: PMC9546775
- DOI: 10.1038/s41587-022-01284-4
Multi-omics single-cell data integration and regulatory inference with graph-linked embedding
Abstract
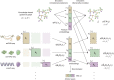
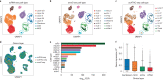
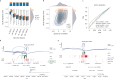
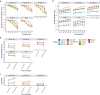
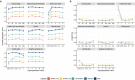
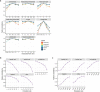
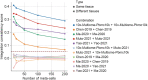
Despite the emergence of experimental methods for simultaneous measurement of multiple omics modalities in single cells, most single-cell datasets include only one modality. A major obstacle in integrating omics data from multiple modalities is that different omics layers typically have distinct feature spaces. Here, we propose a computational framework called GLUE (graph-linked unified embedding), which bridges the gap by modeling regulatory interactions across omics layers explicitly. Systematic benchmarking demonstrated that GLUE is more accurate, robust and scalable than state-of-the-art tools for heterogeneous single-cell multi-omics data. We applied GLUE to various challenging tasks, including triple-omics integration, integrative regulatory inference and multi-omics human cell atlas construction over millions of cells, where GLUE was able to correct previous annotations. GLUE features a modular design that can be flexibly extended and enhanced for new analysis tasks. The full package is available online at https://github.com/gao-lab/GLUE .
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

