Role of p38 MAP kinase in cancer stem cells and metastasis
- PMID: 35501462
- PMCID: PMC9166676
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-022-02329-3
Role of p38 MAP kinase in cancer stem cells and metastasis
Abstract
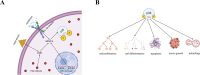
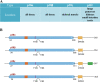
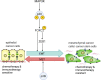
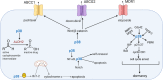
Therapeutic resistance and metastatic progression are responsible for the majority of cancer mortalities. In particular, the development of resistance is a significant barrier to the efficacy of cancer treatments such as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapies. Cancer stem cells (CSCs) underlie treatment resistance and metastasis. p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (p38 MAPK) is downstream of several CSC-specific signaling pathways, and it plays an important role in CSC development and maintenance and contributes to metastasis and chemoresistance. Therefore, the development of therapeutic approaches targeting p38 can sensitize tumors to chemotherapy and prevent metastatic progression.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Sahu V, Nigam L, Agnihotri V, Gupta A, Shekhar S, Subbarao N, et al. Diagnostic significance of p38 isoforms (p38alpha, p38beta, p38gamma, p38delta) in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: comparative serum level evaluation and design of novel peptide inhibitor targeting the same. Cancer Res Treat. 2019;51:313–25. doi: 10.4143/crt.2018.105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

