Integrated analysis of mRNA and long noncoding RNA profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with bronchial asthma
- PMID: 35501805
- PMCID: PMC9059365
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-022-01945-9
Integrated analysis of mRNA and long noncoding RNA profiles in peripheral blood mononuclear cells of patients with bronchial asthma
Abstract
Background: Bronchial asthma is a heterogeneous disease with distinct disease phenotypes and underlying pathophysiological mechanisms. Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) are involved in numerous functionally different biological and physiological processes. The aim of this study was to identify differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs in patients with asthma and further explore the functions and interactions between lncRNAs and mRNAs.
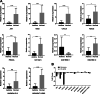
Methods: Ten patients with asthma and 9 healthy controls were enrolled in this study. RNA was isolated from peripheral blood mononuclear cells. We performed microarray analysis to evaluate lncRNA and mRNA expression. The functions of the differentially expressed mRNAs were analyzed by Gene Ontology and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analyses. A global signal transduction network was constructed to identify the core mRNAs. An lncRNA-mRNA network was constructed. Five mRNAs showing the greatest differences in expression levels or high degrees in the gene-gene functional interaction network, with their correlated lncRNAs, were validated by real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction.
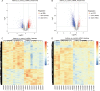
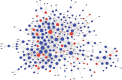
Results: We identified 2229 differentially expressed mRNAs and 1397 lncRNAs between the asthma and control groups. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes pathway analysis identified many pathways associated with inflammation and cell survival. The gene-gene functional interaction network suggested that some core mRNAs are involved in the pathogenesis of bronchial asthma. The lncRNA-mRNA co-expression network revealed correlated lncRNAs. CXCL8, FOXO3, JUN, PIK3CA, and G0S2 and their related lncRNAs NONHSAT115963, AC019050.1, MTCYBP3, KB-67B5.12, and HNRNPA1P12 were identified according to their differential expression levels and high degrees in the gene-gene network.
Conclusions: We identified the core mRNAs and their related lncRNAs and predicted the biological processes and signaling pathways involved in asthma.
Keywords: Bronchial asthma; Long non-coding RNA; Microarray analysis; Peripheral blood mononuclear cell; mRNA.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integrative analysis of the contribution of mRNAs and long non‑coding RNAs to the pathogenesis of asthma.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Sep;20(3):2617-2624. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10511. Epub 2019 Jul 19. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31524265 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profile of long noncoding RNAs in human cerebral aneurysms: a microarray analysis.J Neurosurg. 2017 Nov;127(5):1055-1062. doi: 10.3171/2016.9.JNS16839. Epub 2016 Dec 23. J Neurosurg. 2017. PMID: 28009235
-
Deregulation of lncRNA HIST1H2AG-6 and AIM1-3 in peripheral blood mononuclear cells is associated with newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes.BMC Med Genomics. 2021 Jun 6;14(1):149. doi: 10.1186/s12920-021-00994-z. BMC Med Genomics. 2021. PMID: 34092238 Free PMC article.
-
Unlocking the secrets of long non-coding RNAs in asthma.Thorax. 2022 May;77(5):514-522. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2021-218359. Epub 2022 Mar 4. Thorax. 2022. PMID: 35246486 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comprehensive Analysis of Differentially Expressed lncRNAs in the Perivascular Adipose Tissue of Patients with Coronary Heart Disease.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Oct 11;23(10):341. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2310341. eCollection 2022 Oct. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39077137 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Regulatory Mechanism of CXCL16 Molecule-Related Antigen Presentation Using lncRNA-mRNA Co-Expression Network Analysis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Dec 24;17:11561-11575. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S496133. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39735899 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

