Problem based learning approach increases the academic satisfaction of health science students in Ethiopian universities: a comparative cross sectional study
- PMID: 35501812
- PMCID: PMC9063231
- DOI: 10.1186/s12909-022-03397-5
Problem based learning approach increases the academic satisfaction of health science students in Ethiopian universities: a comparative cross sectional study
Abstract
Background: Problem based learning is being highly implemented in many medical schools worldwide due to its perceived advantages including improvement of problem-solving abilities, development of communication skills, creation and development of critical thinking skill, and making of individuals to be lifelong learners & responsible for their own learning process.
Objective: The study aimed to compare academic satisfaction of Problem and Lecture based learning of regular undergraduate health science students in Ethiopian Universities, 2021.
Method: Institution based comparative cross sectional study was conducted from February 1-30, 2021. Data were collected using a pretested structured and self-administered questionnaire among 850 eligible students from two Universities. Data were entered into EPI info version 6.04 and analyzed using SPSS version 23. Binary Logistic regression model was fitted to identify factors associated with academic satisfaction considering the association to be significant p- value < 0.05.
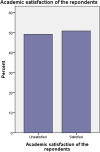
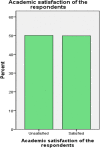
Result: The study result revealed that the magnitude of academic satisfaction among problem based and lecture based learning students were 50.9 and 49.9% respectively. Similarly, problem based learning students were more likely to be academically satisfied than lecture based learning students in their type of curriculum with (AOR = 1.50, 95% CI = 1.02, 2.21). Experience of classroom distress (AOR = 1.93, 95% CI = 1.22, 3.06), quality of teaching (AOR = 0.54, 95% CI = 0.34, 0.86), relationship with classmates (AOR = 0.33, 95% CI = 0.13, 0.80), course content (AOR = 0.56, 95% CI = 0.33, 0.93) and accessibility of technology in the campus (AOR = 0.62, 95% CI = 0.40, 0.96) were the significant factors of academic satisfaction of problem based learning students. Year of study (AOR = 0.29, 95% CI = 0.17, 0.48), quality of teaching (AOR = 0.51, 95% CI = 0.31, 0.85), course content (AOR = 0.59, 95% CI = 0.35, 0.97) and energy & effort (AOR = 0.55, 95% CI = 0.35, 0.88) were significantly associated with academic satisfaction among lecture based learning students.
Conclusion: The study revealed that the academic satisfaction among problem based learning students was higher than lecture based learning students. Incorporating and implementing problem based learning as a formal instructional method in across the universities curriculum is recommended.
Keywords: Academic satisfaction; Comparative cross sectional; Institution based; Lecture based learning; Problem based learning.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no any financial and non-financial competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessing the effectiveness of flipped classroom teaching-learning method among undergraduate medical students at gondar university, college of medicine and health sciences: an interventional study.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Oct 7;24(1):1108. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06105-7. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39375705 Free PMC article.
-
Midwifery students' satisfaction with simulation-based education and associated factors among governmental universities in Amhara region, Ethiopia 2022.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Sep 30;24(1):1070. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05974-2. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39350132 Free PMC article.
-
Magnitude of academic performance and its associated factors among health science students at Eastern Ethiopia University's 2022.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Nov 11;24(1):1288. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-06296-z. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 39529065 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of flipped classrooms to improve learning outcomes in undergraduate health professional education: A systematic review.Campbell Syst Rev. 2023 Jul 7;19(3):e1339. doi: 10.1002/cl2.1339. eCollection 2023 Sep. Campbell Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 37425620 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessment of Problem-Based Learning Acceptance and Associated Factors Among School of Nursing Students at Wachemo University, Central Ethiopia.SAGE Open Nurs. 2025 Feb 4;11:23779608241292420. doi: 10.1177/23779608241292420. eCollection 2025 Jan-Dec. SAGE Open Nurs. 2025. PMID: 39911139 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Implementation of Problem-Based Learning in Undergraduate Medical Education in Ethiopia: An Exploratory Qualitative Study.Adv Med Educ Pract. 2024 Feb 19;15:105-119. doi: 10.2147/AMEP.S443384. eCollection 2024. Adv Med Educ Pract. 2024. PMID: 38404356 Free PMC article.
-
The Benefits of Using Case Study Focussed, Problem Based Learning Approaches to Unit Design for Biomedical Science Students.Br J Biomed Sci. 2023 Jun 29;80:11494. doi: 10.3389/bjbs.2023.11494. eCollection 2023. Br J Biomed Sci. 2023. PMID: 37457621 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of virtual problem-based learning of cardiopulmonary resuscitation on fourth-year nursing students' satisfaction and performance: a quasi-experimental study.BMC Med Educ. 2024 Apr 19;24(1):425. doi: 10.1186/s12909-024-05375-5. BMC Med Educ. 2024. PMID: 38641600 Free PMC article.
-
Study on the Application Value of PBL Combined with Situational Simulation Teaching Method in Clinical Practice Teaching of Radiology Department.Comput Math Methods Med. 2022 Aug 11;2022:6808648. doi: 10.1155/2022/6808648. eCollection 2022. Comput Math Methods Med. 2022. Retraction in: Comput Math Methods Med. 2023 Jun 28;2023:9870342. doi: 10.1155/2023/9870342. PMID: 35991150 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
The impact of self-directed learning experience and course experience on learning satisfaction of university students in blended learning environments: the mediating role of deep and surface learning approach.Front Psychol. 2024 Jan 8;14:1278827. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1278827. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2024. PMID: 38259560 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albarrak AI, Mohammed R, Abalhassan FM, Almutairi KN. Academic satisfaction among traditional and problem based learning medical students. Saudi Med J. 2013;34(11). - PubMed
-
- Marwa Ahmed AE, Wagdy TY, Refaat AH, El-Dinn Ahmed RAG. Measuring students’ satisfaction with implementing a student’ centered seminar at problem-based learning, the Faculty of Medicine - Suez -Canal University. Intel Prop Rights. 2014;2:111.
-
- Mahmood A, Khatoon F, Ali M, Ejaz S, Qureshi AM. Perceptions and Preference of Contemporary Teaching Methods among University Students of Pakistan- A Cross-Sectional Survey, ISSN: 2320–1959. ISBN: 2320–1940. 2012;1(1):06–10.
-
- Al-Naggar AR, Bobryshev VY. Acceptance of problem based learning among medical students. J Community Med Health Educ. 2012;2:5.
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources