Frequency of flash glucose monitoring and glucose metrics: real-world observational data from Saudi Arabia
- PMID: 35501880
- PMCID: PMC9063302
- DOI: 10.1186/s13098-022-00831-y
Frequency of flash glucose monitoring and glucose metrics: real-world observational data from Saudi Arabia
Abstract
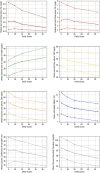
Background: This real-world data study analyzed glucose metrics from FreeStyle Libre® flash glucose monitoring in relation to scanning frequency, time in range (TIR) and estimated A1c (eA1c) in Saudi Arabia.
Methods: Anonymized reader data were analyzed according to scanning frequency quartiles, eA1c categories (<7%,≥7%‒≤9% or>9%) and TIR categories (<50%,≥50%‒≤70% or>70%). Sensors, grouped by reader, were required to have≥120 h of operation. Differences in scanning frequency, eA1c, TIR, time in hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, and glucose variability (standard deviation [SD] and coefficient of variation [CV]) were analyzed between groups.
Results: 6097 readers, 35,747 sensors, and 40 million automatic glucose measurements were analyzed. Patients in the highest scanning frequency quartile (Q4, mean 32.0 scans/day) had lower eA1c (8.47%), greater TIR (46.4%) and lower glucose variation (SD 75.0 mg/dL, CV 38.2%) compared to the lowest quartile (Q1, mean 5.2 scans/day; eA1c 9.77%, TIR 32.8%, SD 94.9 mg/dL, CV 41.3%). Lower eA1c and higher TIR were associated with greater scanning frequency, lower glucose variability and less time in hyperglycemia.
Conclusions: Higher scanning frequency in flash glucose users from Saudi Arabia is associated with lower eA1c, higher TIR, lower glucose variability and less time in hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia.
Keywords: Flash glucose monitoring; FreeStyle Libre®; Real-world data.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Timothy C. Dunn, Kalvin Kao, Laura Brandner, and Manal El Jammal are employees of Abbott Diabetes Care. Mohammad Y. Al-Harbi, Abdulhameed Albunyan, and Ahmed Alnahari report no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Mokdad AH, et al. Cost of diabetes in the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia, 2014. J Diabetes Metab. 2015;6(8):1000575.
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clinical Diabetes. 2008;26(2):77–82. doi: 10.2337/diaclin.26.2.77. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources