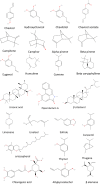
Betelvine (Piper betle L.): A comprehensive insight into its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological, biomedical and therapeutic attributes
- PMID: 35502487
- PMCID: PMC9170825
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.17323
Betelvine (Piper betle L.): A comprehensive insight into its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacological, biomedical and therapeutic attributes
Abstract
Piper betle L. (synonym: Piper betel Blanco), or betel vine, an economically and medicinally important cash crop, belongs to the family Piperaceae, often known as the green gold. The plant can be found all over the world and is cultivatedprimarily in South East Asian countries for its beautiful glossy heart-shaped leaves, which are chewed or consumed as betelquidand widely used in Chinese and Indian folk medicine, as carminative, stimulant,astringent, against parasitic worms, conjunctivitis, rheumatism, wound, etc., andis also used for religious purposes. Hydroxychavicol is the most important bioactive compound among the wide range of phytoconstituents found in essential oil and extracts. The pharmacological attributes of P. betle are antiproliferation, anticancer, neuropharmacological, analgesic, antioxidant, antiulcerogenic, hepatoprotective, antifertility, antibacterial, antifungal and many more. Immense attention has been paid to nanoformulations and their applications. The application of P. betle did not show cytotoxicity in preclinical experiments, suggesting that it could serve as a promising therapeutic candidate for different diseases. The present review comprehensively summarizes the botanical description, geographical distribution, economic value and cultivation, ethnobotanical uses, preclinical pharmacological properties with insights of toxicological, clinical efficacy, and safety of P. betle. The findings suggest that P. betle represents an orally active and safe natural agent that exhibits great therapeutic potential for managing various human medical conditions. However, further research is needed to elucidate its underlying molecular mechanisms of action, clinical aspects, structure-activity relationships, bioavailability and synergistic interactions with other drugs.
Keywords: Betelvine (Piper betle L.); ethnobotany; hydroxychavicol; nanoparticles; pharmacology; phytochemicals.
© 2022 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The underlying mechanism of action for various medicinal properties of Piper betle (betel).Clin Ter. 2015;166(5):208-14. doi: 10.7417/CT.2015.1880. Clin Ter. 2015. PMID: 26550811 Review.
-
Phytochemical composition, β-glucuronidase inhibition, and antioxidant properties of two fractions of Piper betle leaf aqueous extract.J Food Biochem. 2019 Dec;43(12):e13048. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13048. Epub 2019 Oct 3. J Food Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31581322
-
Piper betle (L): Recent Review of Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties, Safety Profiles, and Commercial Applications.Molecules. 2021 Apr 16;26(8):2321. doi: 10.3390/molecules26082321. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33923576 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phytochemical Analysis, Identification and Quantification of Antibacterial Active Compounds in Betel Leaves, Piper betle Methanolic Extract.Pak J Biol Sci. 2017;20(2):70-81. doi: 10.3923/pjbs.2017.70.81. Pak J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29022997
-
Bio-actives of betel leaf (Piper betle L.): A comprehensive review on extraction, isolation, characterization, and biological activity.Phytother Res. 2020 Oct;34(10):2609-2627. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6715. Epub 2020 Jun 11. Phytother Res. 2020. PMID: 32524688 Review.
Cited by
-
Fabrication and characterization of antimicrobial wound dressing nanofibrous materials by PVA-betel leaf extract.Heliyon. 2023 Jul 5;9(7):e17961. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e17961. eCollection 2023 Jul. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37483766 Free PMC article.
-
Quality Control and Authentication of Black Betel Leaf Extract (Piper acre Blume) from East Kalimantan as an Antimicrobial Agent Using a Combination of High-Performance Liquid Chromatography and Chemometric Fourier Transform Infrared.Molecules. 2023 Jul 26;28(15):5666. doi: 10.3390/molecules28155666. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37570633 Free PMC article.
-
A Review of Bioactive Compounds and Antioxidant Activity Properties of Piper Species.Molecules. 2022 Oct 10;27(19):6774. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196774. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36235309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polyphenols and Flavonoids Composition, Anti-Inflammatory and Antioxidant Properties of Andean Baccharis macrantha Extracts.Plants (Basel). 2022 Jun 12;11(12):1555. doi: 10.3390/plants11121555. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35736706 Free PMC article.
-
Phytochemical analysis of leaf extract of Piper nigrum and investigation of its biological activities.Inflammopharmacology. 2025 Jun;33(6):3255-3277. doi: 10.1007/s10787-025-01701-5. Epub 2025 Apr 18. Inflammopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40251438
References
-
- Madhumita M, Guha P, Nag A. Extraction of betel leaves (Piper betle L.) essential oil and its bio‐actives identification: process optimization, GC‐MS analysis and anti‐microbial activity. Ind Crops Prod. 2019;138:111578.
-
- Bajpai V, Sharma D, Kumar B, Madhusudanan KP. Profiling of Piper betle Linn. cultivars by direct analysis in real time mass spectrometric technique. Biomed Chromatogr. 2010;24(12):1283‐1286. - PubMed
-
- Sudjaroen Y. Evaluation of ethnobotanical vegetables and herbs in Samut Songkram province. Procedia Eng. 2012;32:160‐165.
-
- Das S, Parida R, Sandeep IS, Nayak S, Mohanty S. Biotechnological intervention in betelvine (Piper betle L.): a review on recent advances and future prospects. Asian Pacific J Trop Med. 2016;9(10):938‐946. - PubMed
-
- Jane NS, Deshmukh AP, Joshi MS. Review of study of different diseases on betelvine plant and control measure. Int J Appl Innov Eng Manag. 2014;3(3):560‐563.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources