Circular RNA CircSHKBP1 accelerates the proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and stem cell-like properties via modulation of microR-766-5p/high mobility group AT-hook 2 axis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
- PMID: 35502885
- PMCID: PMC9275975
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2068922
Circular RNA CircSHKBP1 accelerates the proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, and stem cell-like properties via modulation of microR-766-5p/high mobility group AT-hook 2 axis in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma
Abstract
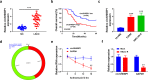
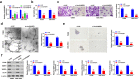
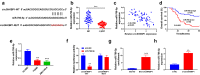
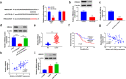
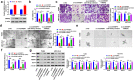
Laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC) is a common malignancy in head and neck. Circular SHKBP1 (circSHKBP) exerts momentous functions in the occurrence of many cancers including LSCC. Thus, we investigated the oncogenic capacities of circSHKBP1 in LSCC, and revealed the underlying mechanism as a competing endogenous RNA. The expression levels of circSHKBP1, miR-766-5p, and high mobility group AT-hook 2 (HMGA2) were examined by quantitative real-time PCR and their influences on the overall survival were measured by Kaplan-Meier method. The correlations between circSHKBP1 and miR-766-5p or HMGA2 were detected by Spearman's rank correlation analysis. In vitro, the influences of circSHKBP1/miR-766-5p/HMGA2 axis on the tumorigenesis of LSCC were examined by CCK-8, transwell, sphere formation, and angiogenesis assays, respectively. circSHKBP1 expression was up-regulated in the LSCC specimens and cell lines. And elevated circSHKBP1 expression was closely linked to poor prognosis. Silencing circSHKBP1 expression restrained cell proliferation, invasion, angiogenesis, stem cell-like properties and tumor growth. We observed that miR-766-5p was down-regulated and negatively correlated to circSHKBP1 in LSCC samples. However, HMGA2 was highly expressed and positively associated with circSHKBP1 in these specimens. Importantly, the levels of circSHKBP1, miR-766-5p, and HMGA2 were closely associated with patients' clinical parameters including lymph nodes metastasis and TNM stages. Mechanistic analysis clarified that circSHKBP1 sponged miR-766-5p to regulate HMGA2, the target of miR-766-5p. Moreover, miR-766-5p inhibition and overexpression of HMGA2 rescued the tumor-suppressing roles of circSHKBP1 downregulation in LSCC. In conclusion, circSHKBP1 accelerated the tumorigenesis of LSCC via modulating HMGA2 by targeting miR-766-5p.
Keywords: CircSHKBP1; HMGA2; MiR-766-5p; laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma; tumorigenesis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures


References
-
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL.. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021;71(3):209–249. - PubMed
-
- Meng WX, Wang BS. Epigenetic regulations in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Lin chuang er bi yan hou tou jing wai ke za zhi = Journal of clinical otorhinolaryngology, head, and neck surgery. 2018;32(22):1958–1762. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2016. CA Cancer J Clin. 2016;66(1):7–30. - PubMed
-
- Bodnar M, Szylberg Ł, Kazmierczak W, et al. Tumor progression driven by pathways activating matrix metalloproteinases and their inhibitors. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015;44(6):437–443. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
