Btg2 mutation induces renal injury and impairs blood pressure control in female rats
- PMID: 35503009
- PMCID: PMC9208437
- DOI: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00167.2021
Btg2 mutation induces renal injury and impairs blood pressure control in female rats
Abstract
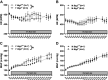
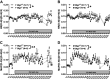
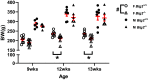
Hypertension (HTN) is a complex disease influenced by heritable genetic elements and environmental interactions. Dietary salt is among the most influential modifiable factors contributing to increased blood pressure (BP). It is well established that men and women develop BP impairment in different patterns and a recent emphasis has been placed on identifying mechanisms leading to the differences observed between the sexes in HTN development. The current work reported here builds on an extensive genetic mapping experiment that sought to identify genetic determinants of salt-sensitive (SS) HTN using the Dahl SS rat. BTG antiproliferation factor 2 (Btg2) was previously identified by our group as a candidate gene contributing to SS HTN in female rats. In the current study, Btg2 was mutated using transcription activator-like effector nuclease (TALEN)-targeted gene disruption on the SSBN congenic rat background. The Btg2 mutated rats exhibited impaired BP and proteinuria responses to a high-salt diet compared with wild-type rats. Differences in body weight, mutant pup viability, skeletal morphology, and adult nephron density suggest a potential role for Btg2 in developmental signaling pathways. Subsequent cell cycle gene expression assessment provides several additional signaling pathways that Btg2 may function through during salt handling in the kidney. The expression analysis also identified several potential upstream targets that can be explored to further isolate therapeutic approaches for SS HTN.
Keywords: TALEN; hypertension; renal; salt sensitivity.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Targeted disruption of regulated endocrine-specific protein ( Resp18) in Dahl SS/Mcw rats aggravates salt-induced hypertension and renal injury.Physiol Genomics. 2018 May 1;50(5):369-375. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00008.2018. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Physiol Genomics. 2018. PMID: 29570433 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of Arhgef11 in the Dahl Salt-Sensitive Rat Protects Against Hypertension-Induced Renal Injury.Hypertension. 2020 Apr;75(4):1012-1024. doi: 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.119.14338. Epub 2020 Mar 9. Hypertension. 2020. PMID: 32148127 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic mutation of recombination activating gene 1 in Dahl salt-sensitive rats attenuates hypertension and renal damage.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Mar 15;304(6):R407-14. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00304.2012. Epub 2013 Jan 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23364523 Free PMC article.
-
[The renal metabolic mechanism of salt sensitive hypertension in Dahl-SS rats].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022 Feb 25;74(1):47-58. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2022. PMID: 35199125 Review. Chinese.
-
Tumor suppressors BTG1 and BTG2: Beyond growth control.J Cell Physiol. 2019 May;234(5):5379-5389. doi: 10.1002/jcp.27407. Epub 2018 Oct 23. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30350856 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Deciphering the molecular nexus of BTG2 in periodontitis and diabetic kidney disease.BMC Med Genomics. 2024 Jun 3;17(1):152. doi: 10.1186/s12920-024-01915-6. BMC Med Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38831322 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors alleviate renal fibrosis in diabetic kidney disease by inhibiting Hmgcs2 and Btg2 in proximal tubular cells.J Transl Med. 2025 Aug 25;23(1):959. doi: 10.1186/s12967-025-06788-6. J Transl Med. 2025. PMID: 40855324 Free PMC article.
-
Btg2 Promotes Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis via Smad3-Dependent Podocyte-Mesenchymal Transition.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 Nov;10(32):e2304360. doi: 10.1002/advs.202304360. Epub 2023 Sep 25. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023. PMID: 37749872 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

