Impact on the Nutritional and Functional Status of Older Mexican Adults in the Absence of Recreational Activities due to COVID-19: A Longitudinal Study From 2018 to 2021
- PMID: 35503553
- PMCID: PMC9066228
- DOI: 10.1177/07334648221099278
Impact on the Nutritional and Functional Status of Older Mexican Adults in the Absence of Recreational Activities due to COVID-19: A Longitudinal Study From 2018 to 2021
Abstract
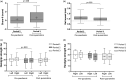
A longitudinal study, from 2018 to 2021, identified impacts on the nutritional and functional status of older adults when face-to-face activities at a social assistance center in Mexico were suspended due to the COVID-19 pandemic. A total of 71 older adults were evaluated at three different periods: 18 months prior, three months before the pandemic, and 12 months after the onset of the pandemic. Seventy-one older adults completed follow up. Anthropometric measurements, dietary intake, physical tests, and health screening for malnutrition, dependence, and physical frailty, were evaluated. There was a significant decrease in lean body mass and body water in the older adults assessed, in addition to a significant reduction in the frailty scale and gait speed. Finally, a significant reduction in ingested energy and several nutrients such as protein, and carbohydrates, was found, yet an increase in sugar and cholesterol intake was noted.
Keywords: COVID-19; functional status; nutritional status; older adults.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Altuna-Venegas S., Aliaga-Vega R., Maguiña J. L., Parodi J. F., Runzer-Colmenares F. M. (2019). Risk of community-acquired pneumonia in older adults with sarcopenia of a hospital from Callao, Peru 2010–2015. Archives of Gerontology and Geriatrics, 82(1), 100-105. 10.1016/j.archger.2019.01.008 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ammar A., Brach M., Trabelsi K., Chtourou H., Boukhris O., Masmoudi L., Bouaziz B., Bentlage E., How D., Ahmed M., Muller P., Muller N., Aloui A., Hammouda O., Paineiras-Domingos L. L., Braakman-Jansen A., Wrede C., Bastoni S., Pernambuco C. S., On Behalf of the ECLB-COVID19 Consortium On Behalf of the ECLB-COVID19 Consortium (2020). Effects of COVID-19 home confinement on eating behavior and physical activity: Results of the ECLB-COVID19 international online survey. Nutrients, 12(6), 1583. 10.3390/nu12061583 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

