Combinational benefit of antihistamines and remdesivir for reducing SARS-CoV-2 replication and alleviating inflammation-induced lung injury in mice
- PMID: 35503561
- PMCID: PMC9113965
- DOI: 10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2021.469
Combinational benefit of antihistamines and remdesivir for reducing SARS-CoV-2 replication and alleviating inflammation-induced lung injury in mice
Abstract
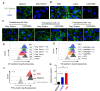
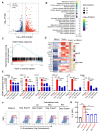
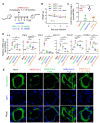
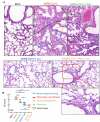
COVID-19 is an immune-mediated inflammatory disease caused by SARS-CoV-2 infection, the combination of anti-inflammatory and antiviral therapy is predicted to provide clinical benefits. We recently demonstrated that mast cells (MCs) are an essential mediator of SARS-CoV-2-initiated hyperinflammation. We also showed that spike protein-induced MC degranulation initiates alveolar epithelial inflammation for barrier disruption and suggested an off-label use of antihistamines as MC stabilizers to block degranulation and consequently suppress inflammation and prevent lung injury. In this study, we emphasized the essential role of MCs in SARS-CoV-2-induced lung lesions in vivo, and demonstrated the benefits of co-administration of antihistamines and antiviral drug remdesivir in SARS-CoV-2-infected mice. Specifically, SARS-CoV-2 spike protein-induced MC degranulation resulted in alveolar-capillary injury, while pretreatment of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells with antihistamines prevented adhesion junction disruption; predictably, the combination of antiviral drug remdesivir with the antihistamine loratadine, a histamine receptor 1 (HR1) antagonist, dampened viral replication and inflammation, thereby greatly reducing lung injury. Our findings emphasize the crucial role of MCs in SARS-CoV-2-induced inflammation and lung injury and provide a feasible combination antiviral and anti-inflammatory therapy for COVID-19 treatment.
新冠肺炎(COVID-19)是由新型冠状病毒(SARS-CoV-2)感染导致的炎症相关疾病。抗病毒药物和抗炎药物联用有望在临床治疗取得有益的效果。我们最近证明,肥大细胞(Mast cell,MC)是SARS-CoV-2引发炎症的重要效应细胞。发现SARS-CoV-2刺突蛋白(Spike)通过诱导MC脱颗粒诱发肺泡上皮细胞炎症从而造成组织通透性破坏,并发现临床上治疗过敏性疾病的抗组胺药物可作为MC稳定剂,阻止Spike诱导的MC脱颗粒,进而抑制炎症发生和保护肺损伤。在该研究中,我们进一步阐述MC在SARS-CoV-2引发肺损伤中的作用,并评价抗组胺药物和抗病毒药物联用对病毒复制和炎症损伤的双重抑制效果。证明Spike诱导的MC脱颗粒可导致肺泡毛细血管损伤,而抗组胺药物预处理肺微血管内皮细胞,可防止细胞间紧密连接的破坏;特别重要一点,发现抗组胺药物HR1(histamine receptor)拮抗剂氯雷他定(Loratadine)和抗病毒药物瑞德西韦(Remdesivir)联用,可同时抑制SARS-CoV-2复制和缓解炎症造成的小鼠肺部损伤。该研究再次证明了MC在SARS-CoV-2诱导肺部炎症和导致肺损伤中的重要作用,并提出一种COVID-19抗病毒药物和抗炎药物联用治疗策略。.
Keywords: Antihistamine; Combinational therapy; Mast cell; Remdesivir; SARS-CoV-2.
Figures

References
-
- Abdelnabi R, Foo CS, Kaptein SJF, Zhang X, Do TND, Langendries L, et al The combined treatment of Molnupiravir and Favipiravir results in a potentiation of antiviral efficacy in a SARS-CoV-2 hamster infection model. eBioMedicine. 2021;72:103595. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2021.103595. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Benfield T, Bodilsen J, Brieghel C, Harboe ZB, Helleberg M, Holm C, et al Improved survival among hospitalized patients with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) treated with remdesivir and dexamethasone. A nationwide population-based cohort study. Clinical Infectious Diseases. 2021;73(11):2031–2036. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab536. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
