Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation: a continuum movens supporting couple sexual dysfunction
- PMID: 35503598
- PMCID: PMC9063256
- DOI: 10.1007/s40618-022-01793-8
Erectile dysfunction and premature ejaculation: a continuum movens supporting couple sexual dysfunction
Abstract
Purpose: The specific underlying mechanisms supporting the association between erectile dysfunction (ED) and premature ejaculation (PE) are still not completely clarified. To summarize and discuss all available data supporting the relationship between PE and ED.
Methods: A comprehensive narrative review was performed. In addition, to better clarify the specific factors underlining ED and PE, a meta-analytic approach of the selected evidence was also performed. In particular, the meta-analytic method was selected in order to minimize possible sources of bias derived from a personal interpretation of the data.
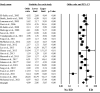
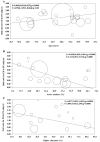
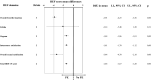
Results: Current data confirm the close association between ED and PE and the bidirectional nature of their relationship. In particular, PE was associated with a fourfold increased risk of ED independently of the definition used. In addition, the risk increased in older patients and in those with lower education, and it was associated with higher anxiety and depressive symptoms. Conversely, ED-related PE was characterized by lower associations with organic parameters such as diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, dyslipidemia and with smoking habit. Finally, when ED was defined according to the International Index of Erectile Function questionnaire, the presence of a stable relationship increased the risk.
Conclusions: ED and PE should be considered in a dimensional prospective way considering the possibility that both clinical entities can overlap and influence each. Correctly recognizing the underlying factors and sexual complaint can help the clinician in deciding the more appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic work-up.
Keywords: Couple; Erectile dysfunction; PDE5i; Premature ejaculation; Sexual desire.
© 2022. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Italian Society of Endocrinology (SIE).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Figures




References
-
- McCabe MP, Sharlip ID, Lewis R, Atalla E, Balon R, Fisher AD, et al. Incidence and prevalence of sexual dysfunction in women and men: a consensus statement from the fourth international consultation on sexual medicine 2015. J Sex Med. 2016;13(2):144–152. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2015.12.034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Salonia A, Bettocchi C, Boeri L, Capogrosso P, Carvalho J, Cilesiz NC, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Sexual and Reproductive Health-2021 Update: Male Sexual Dysfunction. Eur Urol. 2021. - PubMed
-
- Corona G, Rastrelli G, Bartfai G, Casanueva FF, Giwercman A, Antonio L, et al. Self-reported shorter than desired ejaculation latency and related distress-prevalence and clinical correlates: results from the European Male Ageing Study. J Sex Med. 2021;18(5):908–919. doi: 10.1016/j.jsxm.2021.01.187. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

