Nonatherosclerotic Giant Right Coronary Artery Aneurysm
- PMID: 35503700
- PMCID: PMC9054151
- DOI: 10.21470/1678-9741-2020-0649
Nonatherosclerotic Giant Right Coronary Artery Aneurysm
Abstract
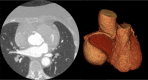
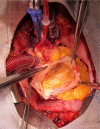
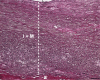
We present an unusual case of a 67-year-old woman with an incidental finding of a cardiac mass on a chest computed tomography. Coronary angiotomography confirmed the diagnosis of right coronary artery aneurysm, with 5.7×5.7 cm. The patient underwent aneurysm resection and coronary bypass surgery, with subsequent histologic study suggestive of arteritis sequelae. Giant coronary artery aneurysms have a high risk of complications and aneurysm exclusion must be beneficial. This is a rare condition that can also be part of a systemic inflammatory disease.
Keywords: Coronary Aneurysm; Coronary Artery Bypass; Coronary Vessels; Incidental Findings; Tomography; X-Ray Computed.
Conflict of interest statement
No conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
