Bacteriophage treatment of disseminated cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection
- PMID: 35504908
- PMCID: PMC9064978
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29689-4
Bacteriophage treatment of disseminated cutaneous Mycobacterium chelonae infection
Abstract
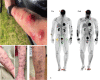
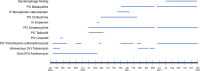
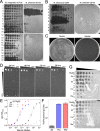
Mycobacterium chelonae is a rare cause of chronic disseminated cutaneous infections in immunocompromised patients. Multidrug-resistant M. chelonae infections present a challenge for treatment, and prolonged antimicrobial courses lead to significant toxicities and further antimicrobial resistance. We report a case of refractory cutaneous disseminated M. chelonae infection in a patient with seronegative arthritis on immunotherapy with tofacitinib that was treated with combination antimicrobial, surgical, and single bacteriophage therapy with excellent clinical response. The patient developed neutralizing antibodies against the bacteriophage but continues to have stable improvement of disease with negative biopsies and no evidence of bacterial resistance to the phage.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
C.A.B. receives contract and grant funding from Gilead. G.F.H. acts as consultant and grant recipient for Janssen pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Wallace RJ, Brown BA, Onyi GO. Skin, soft tissue, and bone infections due to Mycobacterium chelonae chelonae: importance of prior corticosteroid therapy, frequency of disseminated infections, and resistance to oral antimicrobials other than clarithromycin. J. Infect. Dis. 1992;166:405–412. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.405. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

