Multivalent interactions essential for lentiviral integrase function
- PMID: 35504909
- PMCID: PMC9065133
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-022-29928-8
Multivalent interactions essential for lentiviral integrase function
Abstract
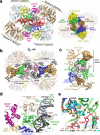
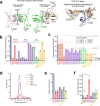
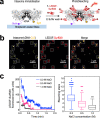
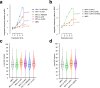
A multimer of retroviral integrase (IN) synapses viral DNA ends within a stable intasome nucleoprotein complex for integration into a host cell genome. Reconstitution of the intasome from the maedi-visna virus (MVV), an ovine lentivirus, revealed a large assembly containing sixteen IN subunits1. Herein, we report cryo-EM structures of the lentiviral intasome prior to engagement of target DNA and following strand transfer, refined at 3.4 and 3.5 Å resolution, respectively. The structures elucidate details of the protein-protein and protein-DNA interfaces involved in lentiviral intasome formation. We show that the homomeric interfaces involved in IN hexadecamer formation and the α-helical configuration of the linker connecting the C-terminal and catalytic core domains are critical for MVV IN strand transfer activity in vitro and for virus infectivity. Single-molecule microscopy in conjunction with photobleaching reveals that the MVV intasome can bind a variable number, up to sixteen molecules, of the lentivirus-specific host factor LEDGF/p75. Concordantly, ablation of endogenous LEDGF/p75 results in gross redistribution of MVV integration sites in human and ovine cells. Our data confirm the importance of the expanded architecture observed in cryo-EM studies of lentiviral intasomes and suggest that this organization underlies multivalent interactions with chromatin for integration targeting to active genes.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
D.J.G. and R.K.M. are named as inventors on a patent application relating to the use of the MVV vectors described in this study. A.N.E. has consulted for ViiV Healthcare Co. on work unrelated to this study. No other authors declare competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- DP1 DA043915/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
- FC001178 /CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001221 /CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- FC001178/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P50 AI150481/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- FC001178 /MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- FC001221 /MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K08 AI122838/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI070042/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- FC001061/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- U54 AI150472/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- FC001221/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- P30 CA014195/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- FC001061 /MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

