Type 2 diabetes medication and HbA1c levels in North Karelia Finland, 2013-2019
- PMID: 35506179
- PMCID: PMC9543455
- DOI: 10.1111/dme.14866
Type 2 diabetes medication and HbA1c levels in North Karelia Finland, 2013-2019
Abstract
Aims: To analyse the prevalence of prescribed medications among people with type 2 diabetes, their relationship to HbA1c levels and transitions between medications.
Methods: The data included all 18- to 85-year-old adults with type 2 diabetes (identified from the electronic health records), who lived in North Karelia, Finland, between 2013 and 2019. Type 2 diabetes medication was defined based on prescriptions. Logistic and linear regressions with generalized estimating equations were used to assess the differences between years.
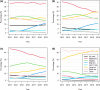
Results: Metformin as a monotherapy was the most used medication (33%-35%) with the largest percentage of those in good glycaemic control. After metformin, the most used medications were long-acting and short-acting insulin and gliptin (16%-24% per group). In insulin groups, there were the smallest percentage of people in good glycaemic control. The use of SGLT2-i increased most during the follow-up (from 1.6% to 11%), but at the same time the percentage of those meeting the target HbA1c level decreased the most (from 83% to 53%). The use of GLP-1 RA and other medications were under 3.5%. SGLT2-i and insulin were the most stable medication groups. The most common transitions were from SGLT2-i to long-acting insulin and between insulin groups.
Conclusions: The sequencing of prescribing additional type 2 diabetes medication or replacing current medication with new ones seems to occur according to guidelines. However, more attention should be paid to the intensification of treatment and the possibilities for new treatment choices in the management of T2D taking into account the persons' characteristics.
Keywords: HbA1c; care; intensification; medicines; treatment; type 2 diabetes.
© 2022 The Authors. Diabetic Medicine published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Diabetes UK.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fowler MJ. Microvascular and macrovascular complications of diabetes. Clin Diabetes. 2008;26(2):77.
-
- American Diabetes Association . Standards of medical care in diabetes‐2019. Diabetes Care. 2019;42(Suppl 1):S11‐S187. - PubMed
-
- Type 2 Diabetes Current Care Guidelines . Working group set up by the Finnish Medical Society Duodecim, the Finnish Society of Internal Medicine and the Finnish Diabetes Association, 2018. Accessed September 6, 2021. https://www.kaypahoito.fi/hoi50056
-
- Davies MJ, D’Alessio DA, Fradkin J, et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2018. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia. 2018;61(12):2461‐2498. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

