Determinants and Temporal Dynamics of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: 14-Year Follow-Up
- PMID: 35506383
- PMCID: PMC9389939
- DOI: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.121.038099
Determinants and Temporal Dynamics of Cerebral Small Vessel Disease: 14-Year Follow-Up
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study is to investigate the temporal dynamics of small vessel disease (SVD) and the effect of vascular risk factors and baseline SVD burden on progression of SVD with 4 neuroimaging assessments over 14 years in patients with SVD.
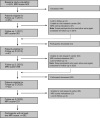
Methods: Five hundred three patients with sporadic SVD (50-85 years) from the ongoing prospective cohort study (RUN DMC [Radboud University Nijmegen Diffusion Tensor and Magnetic Resonance Cohort]) underwent baseline assessment in 2006 and follow-up in 2011, 2015, and 2020. Vascular risk factors and magnetic resonance imaging markers of SVD were evaluated. Linear mixed-effects model and negative binomial regression model were used to examine the determinants of temporal dynamics of SVD markers.
Results: A total of 382 SVD patients (mean [SD] 64.1 [8.4]; 219 men and 163 women) who underwent at least 2 serial brain magnetic resonance imaging scans were included, with mean (SD) follow-up of 11.15 (3.32) years. We found a highly variable temporal course of SVD. Mean (SD) WMH progression rate was 0.6 (0.74) mL/y (range, 0.02-4.73 mL/y) and 13.6% of patients had incident lacunes (1.03%/y) over the 14-year follow-up. About 4% showed net WMH regression over 14 years, whereas 38 out of 361 (10.5%), 5 out of 296 (2%), and 61 out of 231 (26%) patients showed WMH regression for the intervals 2006 to 2011, 2011 to 2015, and 2015 to 2020, respectively. Of these, 29 (76%), 5 (100%), and 57 (93%) showed overall progression across the 14-year follow-up, and the net overall WMH change between first and last scan considering all participants was a net average WMH progression over the 14-year period. Older age was a strong predictor for faster WMH progression and incident lacunes. Patients with mild baseline WMH rarely progressed to severe WMH. In addition, both baseline burden of SVD lesions and vascular risk factors independently and synergistically predicted WMH progression, whereas only baseline SVD burden predicted incident lacunes over the 14-year follow-up.
Conclusions: SVD shows pronounced progression over time, but mild WMH rarely progresses to clinically severe WMH. WMH regression is noteworthy during some magnetic resonance imaging intervals, although it could be overall compensated by progression over the long follow-up.
Keywords: cerebral small vessel disease; magnetic resonance imaging; neuroimaging; risk factor; white matter hyperintensities.
Figures


References
-
- Wardlaw JM, Smith EE, Biessels GJ, Cordonnier C, Fazekas F, Frayne R, Lindley RI, O’Brien JT, Barkhof F, Benavente OR, et al. ; STandards for ReportIng Vascular changes on nEuroimaging (STRIVE v1). Neuroimaging standards for research into small vessel disease and its contribution to ageing and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013;12:822–838. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(13)70124-8 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Pantoni L. Cerebral small vessel disease: from pathogenesis and clinical characteristics to therapeutic challenges. Lancet Neurol. 2010;9:689–701. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(10)70104-6 - PubMed
-
- Schmidt R, Berghold A, Jokinen H, Gouw AA, van der Flier WM, Barkhof F, Scheltens P, Petrovic K, Madureira S, Verdelho A, et al. ; LADIS Study Group. White matter lesion progression in LADIS: frequency, clinical effects, and sample size calculations. Stroke. 2012;43:2643–2647. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.112.662593 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

