Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Nanovesicles as a Credible Agent for Therapy of Pulmonary Hypertension
- PMID: 35507777
- PMCID: PMC12039797
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2021-0415OC
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-derived Nanovesicles as a Credible Agent for Therapy of Pulmonary Hypertension
Abstract
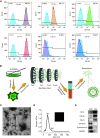
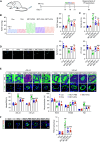
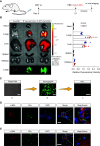
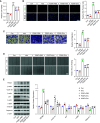
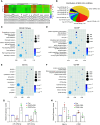
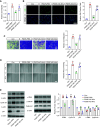
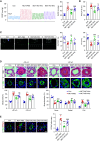
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) derived from mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been evaluated in many studies as promising therapeutic agents for pulmonary hypertension (PH). However, low yields and heterogeneity are major barriers in the translational utility of EVs for clinical studies. To address these limitations, we fabricated MSC-derived nanovesicles (MSC-NVs) by serial extrusion through filters, resulting in MSC-NVs with characteristics similar to conventional EVs but with much higher production yields. Herein, we examined the therapeutic efficacy of MSC-NVs in preclinical models of PH in vitro and in vivo. Intervention with MSC-NVs improved the core pathologies of monocrotaline-induced PH in rats. Intravenous administration of MSC-NVs resulted in significant uptake within hypertensive lungs, pulmonary artery lesions, and especially pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells (PASMCs). In vitro, MSC-NVs inhibited PDGF-induced proliferation, migration, and phenotype switching of PASMCs. miRNA-sequencing analysis of the genetic cargo of MSC-NVs revealed that miR-125b-5p and miR-100-5p are highly abundant, suggesting that they might account for the therapeutic effects of MSC-NVs in PH. Depletion of miR-125b-5p and miR-100-5p in MSCs almost completely abolished the beneficial effects of MSC-NVs in protecting PASMCs from PDGF-stimulated changes in vitro and also diminished the protective effects of MSC-NVs in monocrotaline-induced PH in vivo. These data highlight the efficacy and advantages of MSC-NVs over MSC-EVs as a promising therapeutic strategy against PH.
Keywords: mesenchymal stem cells; miRNAs; nanovesicles; pulmonary artery smooth muscle cells; pulmonary hypertension.
Figures
Comment in
-
Stem Cell-derived Nanovesicles for the Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension: Are We There Yet?Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022 Jul;67(1):3-5. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2022-0078ED. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35522729 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Muhammad SA, Abbas AY, Saidu Y, Fakurazi S, Bilbis LS. Therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stromal cells and secretome in pulmonary arterial hypertension: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Biochimie . 2020;168:156–168. - PubMed
-
- Kanki-Horimoto S, Horimoto H, Mieno S, Kishida K, Watanabe F, Furuya E, et al. Implantation of mesenchymal stem cells overexpressing endothelial nitric oxide synthase improves right ventricular impairments caused by pulmonary hypertension. Circulation . 2006;114(1 Suppl):I181–I185. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

