Marangoni spreading and contracting three-component droplets on completely wetting surfaces
- PMID: 35507868
- PMCID: PMC9171644
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2120432119
Marangoni spreading and contracting three-component droplets on completely wetting surfaces
Abstract
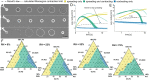
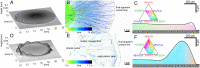
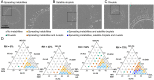
SignificanceThe shape and dynamics of small sessile droplets are dictated by capillary forces. For liquid mixtures, evaporation adds spatio-temporal modulation to these forces that can either enhance or inhibit droplet spreading, depending on the direction of the resulting Marangoni flow. This work experimentally and numerically demonstrates the coexistence of two antagonistic Marangoni flows in a ternary mixture. Played against each other, they can choreograph a boomerang-like wetting motion: Droplets initially rapidly spread, then contract into a compact cap shape. While such a behavior has been impossible in wetting scenarios of simple liquids, it enables spread-retract-remove surface processing with the addition of a single small liquid volume, demonstrated here in a surface-cleaning experiment.
Keywords: Marangoni stress; evaporating droplet; multicomponent droplet; surface cleaning; surface wetting.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interest.
Figures

References
-
- Wenzel R. N., Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. Ind. Eng. Chem. 28, 988–994 (1936).
-
- Zhang X., Shi F., Niu J., Jiang Y., Wang Z., Superhydrophobic surfaces: From structural control to functional application. J. Mater. Chem. 18, 621–633 (2008).
-
- Daniel S., Chaudhury M. K., Chen J. C., Fast drop movements resulting from the phase change on a gradient surface. Science 291, 633–636 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Butler Ellis M. C., Tuck C. R., Miller P. C., How surface tension of surfactant solutions influences the characteristics of sprays produced by hydraulic nozzles used for pesticide application. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 180, 267–276 (2001).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

