Protective effect of polysaccharides isolated from the seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lam. on 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice
- PMID: 35507968
- PMCID: PMC9064182
- DOI: 10.1590/acb370204
Protective effect of polysaccharides isolated from the seeds of Cuscuta chinensis Lam. on 5-fluorouracil-induced intestinal mucositis in mice
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the protective effect of Cuscuta chinensis Lam. polysaccharides (PCCL) on 5-fluorouracil-(5-FU)-induced intestinal mucositis (IM) in mice.
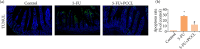
Methods: PCCL was orally administered at a dose of 20 mg·kg-1 for 7 days and its protective effect on 5-FU-induced IM (5-FU, 50 mg·kg-1 for 5 days) was evaluated by monitoring changes in body weight, degree of diarrhea, levels of tissue inflammatory factors (tumor necrosis factor α, interleukin 6, and interleukin 1β levels), apoptosis rates, and the expression levels of caspase-3, Bax and Bcl-2.
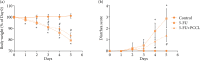
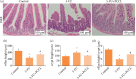
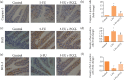
Results: The severity of mucosal injury (as reflected by body weight changes, degree of diarrhea, height of villi, and damage to crypts) was significantly attenuated by PCCL administration. PCCL also reduced the levels of tissue inflammatory factors, the apoptosis rate, and the expression of caspase-3 and Bax, and increased Bcl-2 expression.
Conclusions: PCCL administration may be significantly protective against 5-FU-induced IM by inhibiting apoptosis and regulating the abnormal inflammation associated with it.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: Nothing to declare.
Figures

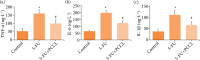
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

