Polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid-derived lipid mediators: Recent advances in the understanding of their biosynthesis, structures, and functions
- PMID: 35508275
- PMCID: PMC9346631
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2022.101165
Polyunsaturated fatty acids and fatty acid-derived lipid mediators: Recent advances in the understanding of their biosynthesis, structures, and functions
Abstract
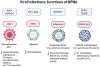
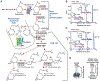
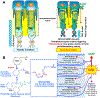
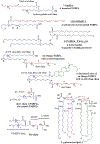
Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are structural components of membrane phospholipids, and influence cellular function via effects on membrane properties, and also by acting as a precursor pool for lipid mediators. These lipid mediators are formed via activation of pathways involving at least one step of dioxygen-dependent oxidation, and are consequently called oxylipins. Their biosynthesis can be either enzymatically-dependent, utilising the promiscuous cyclooxygenase, lipoxygenase, or cytochrome P450 mixed function oxidase pathways, or nonenzymatic via free radical-catalyzed pathways. The oxylipins include the classical eicosanoids, comprising prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, and also more recently identified lipid mediators. With the advent of new technologies there is growing interest in identifying these different lipid mediators and characterising their roles in health and disease. This review brings together contributions from some of those at the forefront of research into lipid mediators, who provide brief introductions and summaries of current understanding of the structure and functions of the main classes of nonclassical oxylipins. The topics covered include omega-3 and omega-6 PUFA biosynthesis pathways, focusing on the roles of the different fatty acid desaturase enzymes, oxidized linoleic acid metabolites, omega-3 PUFA-derived specialized pro-resolving mediators, elovanoids, nonenzymatically oxidized PUFAs, and fatty acid esters of hydroxy fatty acids.
Keywords: Elovanoids; FAHFA; Fatty acid desaturase; Lipid mediators; Maresins; Omega-3 PUFA; Oxylipins; Protectins; Resolvins; SPM.
Copyright © 2022 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
N.G. Bazan is the founder of two start-up companies that have exclusively licensed technologies from LSUHSC involving elovanoids and related lipids for clinical applications: NeuResto Therapeutics, LLC and CurVirBiotech, LLC. All other authors declare no conflicts of financial interest.
Figures





References
-
- Gomez-Larrauri A, Presa N, Dominguez-Herrera A, Ouro A, Trueba M, Gomez-Munoz A. Role of bioactive sphingolipids in physiology and pathology. Essays Biochem 2020;64(3):579–89. - PubMed
-
- Hannun YA, Obeid LM. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2008;9(2):139–50. - PubMed
-
- Shimizu T Lipid mediators in health and disease: enzymes and receptors as therapeutic targets for the regulation of immunity and inflammation. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 2009;49:123–50. - PubMed
-
- von Euler US. History and development of prostaglandins. Gen Pharmacol 1983; 14(1):3–6. - PubMed

